Page 71 - Read Online
P. 71
Page 12 of 15 Kato et al. Hepatoma Res 2021;7:10 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.129
Figure 5. Overall and disease-free survivals after the first RLR in 46 patients with HCC. (A) overall survival (OS); (B) disease-free
survival (DFS)
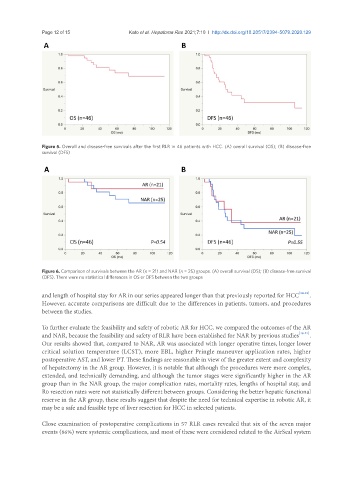
Figure 6. Comparison of survivals between the AR (n = 21) and NAR (n = 25) groups. (A) overall survival (OS); (B) disease-free survival
(DFS). There were no statistical differences in OS or DFS between the two groups
and length of hospital stay for AR in our series appeared longer than that previously reported for HCC [20-22] .
However, accurate comparisons are difficult due to the differences in patients, tumors, and procedures
between the studies.
To further evaluate the feasibility and safety of robotic AR for HCC, we compared the outcomes of the AR
and NAR, because the feasibility and safety of RLR have been established for NAR by previous studies [18-21] .
Our results showed that, compared to NAR, AR was associated with longer operative times, longer lower
critical solution temperature (LCST), more EBL, higher Pringle maneuver application rates, higher
postoperative AST, and lower PT. These findings are reasonable in view of the greater extent and complexity
of hepatectomy in the AR group. However, it is notable that although the procedures were more complex,
extended, and technically demanding, and although the tumor stages were significantly higher in the AR
group than in the NAR group, the major complication rates, mortality rates, lengths of hospital stay, and
R0 resection rates were not statistically different between groups. Considering the better hepatic functional
reserve in the AR group, these results suggest that despite the need for technical expertise in robotic AR, it
may be a safe and feasible type of liver resection for HCC in selected patients.
Close examination of postoperative complications in 57 RLR cases revealed that six of the seven major
events (86%) were systemic complications, and most of these were considered related to the AirSeal system