Page 73 - Read Online
P. 73
Page 8 of 18 Lee et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:51 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.78
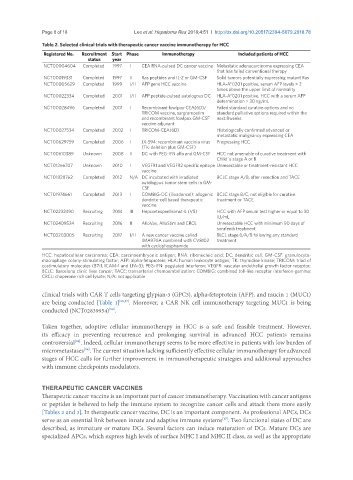
Table 2. Selected clinical trials with therapeutic cancer vaccine immunotherapy for HCC
Registered No. Recruitment Start Phase Immunotherapy Included patients of HCC
status year
NCT00004604 Completed 1997 I CEA RNA-pulsed DC cancer vaccine Metastatic adenocarcinoma expressing CEA
that has failed conventional therapy
NCT00019331 Completed 1997 II Ras peptides and IL-2 or GM-CSF Solid tumors potentially expressing mutant Ras
NCT00005629 Completed 1999 I/II AFP gene HCC vaccine HLA-A*0201 positive, serum AFP levels > 2
times above the upper limit of normality
NCT00022334 Completed 2001 I/II AFP peptide-pulsed autologous DC HLA-A*0201 positive, HCC with a serum AFP
determination > 30 ng/mL
NCT00028496 Completed 2001 I Recombinant fowlpox-CEA(6D)/ Failed standard curative options and no
TRICOM vaccine, sargramostim standard palliative options required within the
and recombinant fowlpox GM-CSF next 8weeks
vaccine adjuvant
NCT00027534 Completed 2002 I TRICOM-CEA(6D) Histologically confirmed advanced or
metastatic malignancy expressing CEA
NCT00629759 Completed 2006 I JX-594: recombinant vaccinia virus Progressing HCC
(TK-deletion plus GM-CSF)
NCT00610389 Unknown 2008 II DC with PEG-IFN alfa and GM-CSF HCC not amenable of curative treatment with
Child´s stage A or B
NCT01266707 Unknown 2010 I VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 specific epitope Unresectable or treatment-resistant HCC
vaccine
NCT01828762 Completed 2012 N/A DC incubated with irradiated BCLC stage A/B, after resection and TACE
autologous tumor stem cells in GM-
CSF
NCT01974661 Completed 2013 I COMBIG-DC (ilixadencel): allogenic BCLC stage B/C, not eligible for curative
dendrite-cell based therapeutic treatment or TACE
vaccine
NCT02232490 Recruiting 2014 III Hepcortespenlisimut-L (V5) HCC with AFP serum test higher or equal to 30
IU/mL
NCT02409524 Recruiting 2016 II AlloVax, AlloStim and CRCL Unresectable HCC with minimum 90 days of
sorafenib treatment
NCT03203005 Recruiting 2017 I/II A new cancer vaccine called BLCL stage 0/A/B following any standard
IMA970A combined with CV8102 treatment
with cyclophosphamide
HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; CEA: carcinoembryonic antigen; RNA: ribonucleic acid; DC: dendritic cell; GM-CSF: granulocyte-
macrophage colony-stimulating factor; AFP: alpha-fetoprotein; HLA: human leukocyte antigen; TK: thymidine kinase; TRICOM: triad of
costimulatory molecules (B7-1, ICAM-1 and LFA-3); PEG-IFN: pegylated interferon; VEGFR: vascular endothelial growth factor receptor;
BCLC: Barcelona clinic liver cancer; TACE: transarterial chemoembolization; COMBIG: combined toll-like receptor interferon-gamma;
CRCL: chaperone rich cell lysate; N/A: not applicable
clinical trials with CAR T cells targeting glypian-3 (GPC3), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), and mucin 1 (MUC1)
are being conducted [Table 1] [56,57] . Moreover, a CAR NK cell immunotherapy targeting MUC1 is being
conducted (NCT02839954) .
[58]
Taken together, adoptive cellular immunotherapy in HCC is a safe and feasible treatment. However,
its efficacy in preventing recurrence and prolonging survival in advanced HCC patients remains
controversial . Indeed, cellular immunotherapy seems to be more effective in patients with low burden of
[59]
micrometastases . The current situation lacking sufficiently effective cellular immunotherapy for advanced
[36]
stages of HCC calls for further improvement in immunotherapeutic strategies and additional approaches
with immune checkpoints modulators.
THERAPEUTIC CANCER VACCINES
Therapeutic cancer vaccine is an important part of cancer immunotherapy. Vaccination with cancer antigens
or peptides is believed to help the immune system to recognize cancer cells and attack them more easily
[Tables 2 and 3]. In therapeutic cancer vaccine, DC is an important component. As professional APCs, DCs
serve as an essential link between innate and adaptive immune systems . Two functional states of DC are
[17]
described, as immature or mature DCs. Several factors can induce maturation of DCs. Mature DCs are
specialized APCs, which express high levels of surface MHC I and MHC II class, as well as the appropriate