Page 56 - Read Online
P. 56
Chan et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:5 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2017.49 Page 9 of 17
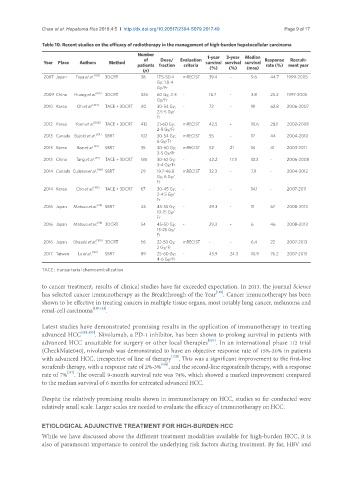
Table 10. Recent studies on the efficacy of radiotherapy in the management of high-burden hepatocellular carcinoma
Number 1-year 3-year Median
of Dose/ Evaluation Response Recruit-
Year Place Authors Method survival survival survival
patients fraction criteria (%) (%) (mos) rate (%) ment year
(n)
2007 Japan Toya et al. [103] 3DCRT 38 17.5-50.4 mRECIST 39.4 - 9.6 44.7 1999-2005
Gy; 1.8-4
Gy/Fr
2009 China Huang et al. [83] 3DCRT 326 60 Gy; 2-3 - 16.7 - 3.8 25.2 1997-2005
Gy/Fr
2010 Korea Oh et al. [104] TACE + 3DCRT 40 30-54 Gy; - 72 - 19 62.8 2006-2007
2.5-5 Gy/
Fr
2012 Korea Yoon et al. [108] TACE + 3DCRT 412 21-60 Gy; mRECIST 42.5 - 10.6 28.1 2002-2008
2-5 Gy/Fr
2013 Canada Bujold et al. [101] SBRT 102 30-54 Gy; mRECIST 55 - 17 44 2004-2010
6 Gy/Fr
2013 Korea Bae et al. [99] SBRT 35 30-60 Gy; mRECIST 52 21 14 41 2003-2011
3-5 Gy/Fr
2013 China Tang et al. [54] TACE + 3DCRT 185 30-52 Gy; - 42.2 17.3 12.3 - 2006-2008
3-4 Gy/Fr
2014 Canada Culleton et al. [100] SBRT 29 19.7-46.8 mRECIST 32.3 - 7.9 - 2004-2012
Gy; 6 Gy/
Fr
2014 Korea Cho et al. [105] TACE + 3DCRT 67 30-45 Gy; - - - 14.1 - 2007-2011
2-4.5 Gy/
Fr
2016 Japan Matsuo et al. [98] SBRT 43 45-55 Gy; - 49.3 - 11 67 2008-2013
10-15 Gy/
Fr
2016 Japan Matsuo et al. [98] 3DCRT 54 45-50 Gy; - 29.3 - 6 46 2008-2013
15-25 Gy/
Fr
2016 Japan Okazaki et al. [109] 3DCRT 56 22-50 Gy; mRECIST - - 6.4 22 2007-2013
2 Gy/Fr
2017 Taiwan Lo et al. [102] SBRT 89 25-60 Gy; - 45.9 24.3 10.9 76.2 2007-2015
4-6 Gy/Fr
TACE: transarterial chemoembolization
to cancer treatment, results of clinical studies have far exceeded expectation. In 2013, the journal Science
[118]
has selected cancer immunotherapy as the Breakthrough of the Year . Cancer immunotherapy has been
shown to be effective in treating cancers in multiple tissue organs, most notably lung cancer, melanoma and
renal-cell carcinoma [119-121] .
Latest studies have demonstrated promising results in the application of immunotherapy in treating
advanced HCC [122,123] . Nivolumab, a PD-1 inhibitor, has been shown to prolong survival in patients with
advanced HCC unsuitable for surgery or other local therapies [123] . In an international phase 1/2 trial
(CheckMate040), nivolumab was demonstrated to have an objective response rate of 15%-20% in patients
[123]
with advanced HCC, irrespective of line of therapy . This was a significant improvement to the first-line
[110]
sorafenib therapy, with a response rate of 2%-3% , and the second-line regorafenib therapy, with a response
[117]
rate of 7% . The overall 9-month survival rate was 74%, which showed a marked improvement compared
to the median survival of 6 months for untreated advanced HCC.
Despite the relatively promising results shown in immunotherapy on HCC, studies so far conducted were
relatively small scale. Larger scales are needed to evaluate the efficacy of immunotherapy on HCC.
ETIOLOGICAL ADJUNCTIVE TREATMENT FOR HIGH-BURDEN HCC
While we have discussed above the different treatment modalities available for high-burden HCC, it is
also of paramount importance to control the underlying risk factors during treatment. By far, HBV and