Page 53 - Read Online
P. 53
Page 6 of 17 Chan et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:5 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2017.49
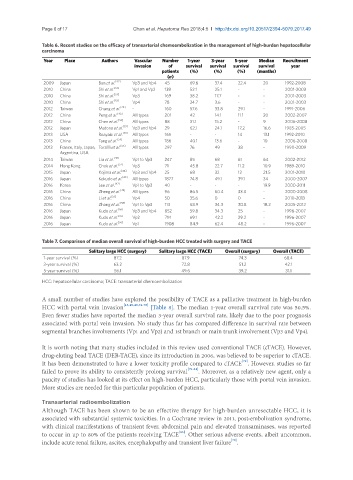
Table 6. Recent studies on the efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization in the management of high-burden hepatocellular
carcinoma
Year Place Authors Vascular Number 1-year 3-year 5-year Median Recruitment
invasion of survival survival survival survival year
patients (%) (%) (%) (months)
(n)
2009 Japan Ban et al. [42] Vp3 and Vp4 45 69.6 37.4 22.4 20 1992-2008
2010 China Shi et al. [53] Vp1 and Vp2 139 52.1 25.1 - - 2001-2003
2010 China Shi et al. [53] Vp3 169 38.2 17.7 - - 2001-2003
2010 China Shi et al. [53] Vp4 78 24.7 3.6 - - 2001-2003
2012 Taiwan Chang et al. [28] - 160 57.6 33.8 29.1 - 1991-2006
2012 China Peng et al. [43] All types 201 42 14.1 11.1 20 2002-2007
2012 China Chen et al. [50] All types 88 31.1 15.2 - 9 2006-2008
2012 Japan Matono et al. [52] Vp3 and Vp4 29 62.1 24.1 17.2 16.6 1985-2005
2013 USA Roayaie et al. [46] All types 165 - - 14 13.1 1992-2010
2013 China Tang et al. [54] All types 186 40.1 13.6 - 10 2006-2008
2013 France, Italy, Japan, Torzilli et al. [55] All types 297 76 49 38 - 1990-2009
Argentina, USA
2014 Taiwan Liu et al. [48] Vp1 to Vp3 247 85 68 61 64 2002-2012
2014 Hong Kong Chok et al. [57] Vp3 71 45.8 22.7 11.2 10.9 1989-2010
2015 Japan Kojima et al. [44] Vp3 and Vp4 25 68 32 12 21.5 2001-2010
2016 Japan Kokudo et al. [45] All types 1877 74.8 49.1 39.1 34 2000-2007
2016 Korea Lee et al. [47] Vp1 to Vp3 40 - - - 19.9 2000-2011
2016 China Zheng et al. [49] All types 96 86.5 60.4 33.3 - 2000-2008
2016 China Li et al. [51] Vp4 50 35.6 0 0 - 2010-2013
2016 China Zhang et al. [58] Vp1 to Vp3 113 68.9 34.3 30.8 18.2 2005-2012
2016 Japan Kudo et al. [56] Vp3 and Vp4 852 59.8 34.3 25 - 1996-2007
2016 Japan Kudo et al. [56] Vp2 714 69.1 42.2 29.2 - 1996-2007
2016 Japan Kudo et al. [56] Vp1 1908 84.9 62.4 48.2 - 1996-2007
Table 7. Comparison of median overall survival of high-burden HCC treated with surgery and TACE
Solitary large HCC (surgery) Solitary large HCC (TACE) Overall (surgery) Overall (TACE)
1-year survival (%) 87.2 87.9 74.3 68.4
3-year survival (%) 63.2 72.8 51.2 42.1
5-year survival (%) 56.1 49.6 39.2 31.1
HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; TACE: transarterial chemoembolization
A small number of studies have explored the possibility of TACE as a palliative treatment in high-burden
HCC with portal vein invasion [43,48,49,74-78] [Table 8]. The median 1-year overall survival rate was 50.5%.
Even fewer studies have reported the median 3-year overall survival rate, likely due to the poor prognosis
associated with portal vein invasion. No study thus far has compared difference in survival rate between
segmental branches involvements (Vp1 and Vp2) and 1st branch or main trunk involvement (Vp3 and Vp4).
It is worth noting that many studies included in this review used conventional TACE (cTACE). However,
drug-eluting bead TACE (DEB-TACE), since its introduction in 2006, was believed to be superior to cTACE.
[79]
It has been demonstrated to have a lower toxicity profile compared to cTACE . However, studies so far
failed to prove its ability to consistently prolong survival [79-84] . Moreover, as a relatively new agent, only a
paucity of studies has looked at its effect on high-burden HCC, particularly those with portal vein invasion.
More studies are needed for this particular population of patients.
Transarterial radioembolization
Although TACE has been shown to be an effective therapy for high-burden unresectable HCC, it is
associated with substantial systemic toxicities. In a Cochrane review in 2011, post-embolization syndrome,
with clinical manifestations of transient fever, abdominal pain and elevated transaminases, was reported
[85]
to occur in up to 80% of the patients receiving TACE . Other serious adverse events, albeit uncommon,
[79]
include acute renal failure, ascites, encephalopathy and transient liver failure .