Page 151 - Read Online
P. 151
Yang et al. Hepatoma Res 2023;9:48 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2023.68 Page 3 of 21
Table 1. Common genomic alterations and frequency (%) in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Kendre et al. Verdaguer et al. Wang et al. Carapeto et al. Cleary et al. Lowery et al.
Target [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13]
2023 (n = 6130) 2022 (n = 258) 2022 (n = 805) 2021 (n = 96) 2021 (n = 178) 2018 (n = 158)
ARID1A 17.9 18.1 13.0 19.0 NA 23.0
BAP1 13.6 13.5 11.7 17.0 NA 18.9
BRAF V600E 5.0 4.3 NA 2.0 3.4 NA
BRCA1/2 3.4 3.1 NA NA 1.7 NA
CDKN2A 30.2 NA 6.1 3.0 NA NA
HER2 5.1 1.6 NA NA 1.7 NA
FGFR2 11.6 8.0 11.4 10.0 11.8 12.7
IDH1 14.3 23.1 NA 24.0 18.5 29.1
IDH2 4.0 7.2 NA 6.0 4.5 NA
IDH1/2 25.9 31.1 14.8 34.0 30.3 NA
KRAS 20.1 11.5 NA 6.0 17.3 7.0
MDM2 4.3 NA NA NA NA NA
MET 2.2 2.4 NA NA NA NA
PBRM1 11.3 NA 8.3 7.0 NA NA
PIK3CA 6.5 7.7 5.7 1.0 NA NA
RET NA NA NA NA 0.6 NA
SMAD4 7.1 NA NA NA NA 5.1
TP53 33.7 NA 22.0 NA NA 17.8
TMB-high 3.7 NA NA NA NA NA
NA: not available.
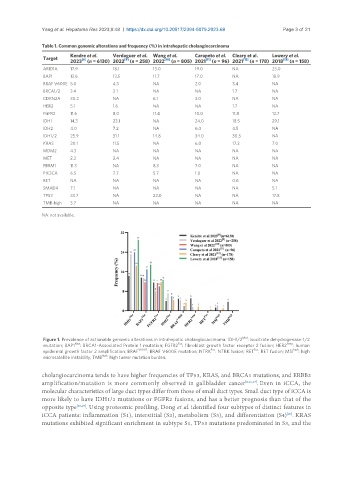
Figure 1. Prevalence of actionable genomic alterations in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. IDH1/2 Mut : isocitrate dehydrogenase-1/2
Fus
mutation; BAP1 Mut : BRCA1-Associated Protein 1 mutation; FGFR2 : fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 fusion; HER2 Amp : human
Fus
Fus
epidermal growth factor 2 amplification; BRAF V600E : BRAF V600E mutation; NTRK : NTRK fusion; RET : RET fusion; MSI high : high
microsatellite instability; TMB high : high tumor mutation burden.
cholangiocarcinoma tends to have higher frequencies of TP53, KRAS, and BRCA1 mutations, and ERBB2
amplification/mutation is more commonly observed in gallbladder cancer [8,16,17] . Even in iCCA, the
molecular characteristics of large duct types differ from those of small duct types. Small duct type of iCCA is
more likely to have IDH1/2 mutations or FGFR2 fusions, and has a better prognosis than that of the
opposite type [18,19] . Using proteomic profiling, Dong et al. identified four subtypes of distinct features in
iCCA patients: inflammation (S1), interstitial (S2), metabolism (S3), and differentiation (S4) . KRAS
[20]
mutations exhibited significant enrichment in subtype S1, TP53 mutations predominated in S3, and the