Page 117 - Read Online
P. 117
Page 18 of 23 Thonglert et al. Hepatoma Res 2023;9:40 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2023.47
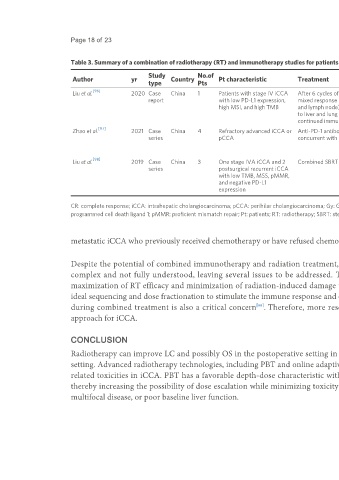
Table 3. Summary of a combination of radiotherapy (RT) and immunotherapy studies for patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA)
Study No.of Systemic treatment
Author yr Country Pt characteristic Treatment RT details Treatment outcomes Toxicity
type Pts details
[96]
Liu et al. 2020 Case China 1 Patients with stage IV iCCA After 6 cycles of immunotherapy, SBRT with a total pembrolizumab CR; The patient patient No
report with low PD-L1 expression, mixed response (PD lung, PR liver, dose of 50 Gy to has survived 26 months significant
high MSI, and high TMB and lymph node), so received SBRT the liver and 48 after combined toxicity
to liver and lung lesion, and Gy to the lung treatment and remains reported
continued immunotherapy tumor-free
[97]
Zhao et al. 2021 Case China 4 Refractory advanced iCCA or Anti-PD-1 antibody following or SBRT Nivolumab (n = 2); CR in 1 patient; PR in 2 No
series pCCA concurrent with SBRT Pembrolizumab (n = 1); patients; SD in 1 patient; significant
Pembrolizumab + One unresectable toxicity
Everoliumus (n = 1) patient became operable reported
[98]
Liu et al. 2019 Case China 3 One stage IVA iCCA and 2 Combined SBRT with PD-1 blocker SBRT 52-55 Gy Nivolumab (n = 1); CR in 1 patient; PR in 2 No
series postsurgical recurrent iCCA in 4-5 Fractions Pembrolizumab (n = 2) patients significant
with low TMB, MSS, pMMR, toxicity
and negative PD-L1 reported
expression
CR: complete response; iCCA: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; pCCA: perihilar cholangiocarcinoma; Gy: Gray; MSI: microsatellite instability; MSS: microsatellite stable; No.: number; PD: progressive disease; PD-L1:
programmed cell death ligand 1; pMMR: proficient mismatch repair; Pt: patients; RT: radiotherapy; SBRT: stereotactic body radiotherapy; SD: stable disease; TMB: tumor mutation burden.
metastatic iCCA who previously received chemotherapy or have refused chemotherapy.
Despite the potential of combined immunotherapy and radiation treatment, numerous challenges remain. The synergistic effect between RT and ICIs is
complex and not fully understood, leaving several issues to be addressed. These include determining the optimal volume of irradiation to balance the
maximization of RT efficacy and minimization of radiation-induced damage to circulating lymphocytes and the adaptive immune response. Moreover, the
ideal sequencing and dose fractionation to stimulate the immune response and overcome resistance is yet to be identified. Ensuring the safety of normal tissues
[99]
during combined treatment is also a critical concern . Therefore, more research is needed to better understand and optimize this combined treatment
approach for iCCA.
CONCLUSION
Radiotherapy can improve LC and possibly OS in the postoperative setting in patients with high-risk features as well as in the locally advanced unresectable
setting. Advanced radiotherapy technologies, including PBT and online adaptive MRgRT, can potentially improve treatment outcomes and reduce treatment-
related toxicities in iCCA. PBT has a favorable depth-dose characteristic with the Bragg peak, which can reduce low-dose spillage to surrounding organs,
thereby increasing the possibility of dose escalation while minimizing toxicity. The benefits of PBT may be more pronounced in patients with large tumors,
multifocal disease, or poor baseline liver function.