Page 119 - Read Online
P. 119
Thonglert et al. Hepatoma Res 2023;9:40 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2023.47 Page 19 of 23
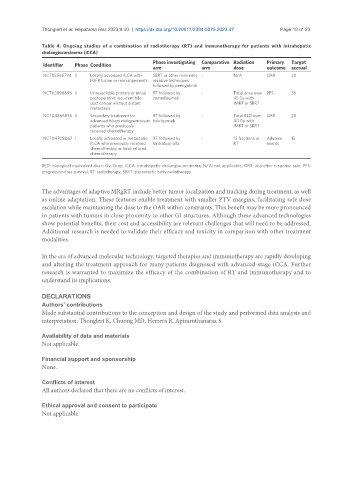
Table 4. Ongoing studies of a combination of radiotherapy (RT) and immunotherapy for patients with intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA)
Phase investigating Comparative Radiation Primary Target
Identifier Phase Condition
arm arm dose outcome accrual
NCT05565794 II Locally advanced iCCA with SBRT or other minimally - N/A ORR 20
FGFR fusion or rearrangements invasive techniques
followed by pemigatinib
NCT03898895 II Unresectable primary or initial RT followed by - Total dose over PFS 36
postoperative recurrent bile camrelizumab 45 Gy with
duct cancer without distant IMRT or SBRT
metastasis
NCT04866836 II Secondary treatment for RT followed by - Total BED over ORR 20
advanced biliary malignancies in tislelizumab 40 Gy with
patients who previously IMRT or SBRT
received chemotherapy
NCT04708067 I Locally advanced or metastatic RT followed by - 15 fractions or Adverse 15
iCCA who previously received bintrafusp alfa RT events
chemotherapy or have refused
chemotherapy.
BED: biological equivalent dose; Gy: Gray; iCCA: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; N/A: not applicable; ORR: objective response rate; PFS:
progression-free survival; RT: radiotherapy; SBRT: stereotactic body radiotherapy.
The advantages of adaptive MRgRT include better tumor localization and tracking during treatment, as well
as online adaptation. These features enable treatment with smaller PTV margins, facilitating safe dose
escalation while maintaining the dose to the OAR within constraints. This benefit may be more pronounced
in patients with tumors in close proximity to other GI structures. Although these advanced technologies
show potential benefits, their cost and accessibility are relevant challenges that will need to be addressed.
Additional research is needed to validate their efficacy and toxicity in comparison with other treatment
modalities.
In the era of advanced molecular technology, targeted therapies and immunotherapy are rapidly developing
and altering the treatment approach for many patients diagnosed with advanced-stage iCCA. Further
research is warranted to maximize the efficacy of the combination of RT and immunotherapy and to
understand its implications.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the study and performed data analysis and
interpretation: Thonglert K, Chuong MD, Herrera R, Apisarnthanarax S
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Financial support and sponsorship
None.
Conflicts of interest
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.