Page 67 - Read Online
P. 67
Rutter et al. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucleic Acids 2023;4:90-106 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/evcna.2023.04 Page 98
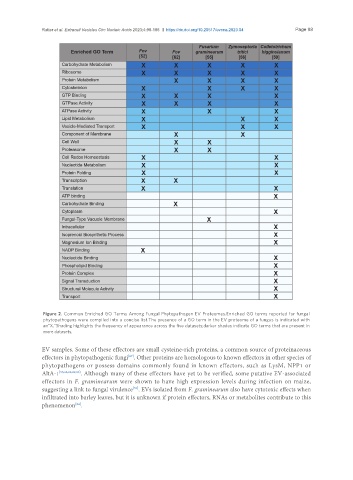
Figure 2. Common Enriched GO Terms Among Fungal Phytopathogen EV Proteomes.Enriched GO terms reported for fungal
phytopathogens were compiled into a concise list.The presence of a GO term in the EV proteome of a fungus is indicated with
an"X."Shading highlights the frequency of appearance across the five datasets;darker shades indicate GO terms that are present in
more datasets.
EV samples. Some of these effectors are small cysteine-rich proteins, a common source of proteinaceous
effectors in phytopathogenic fungi . Other proteins are homologous to known effectors in other species of
[87]
phytopathogens or possess domains commonly found in known effectors, such as LysM, NPP1 or
AltA-1 [55,62,88,89,90] . Although many of these effectors have yet to be verified, some putative EV-associated
effectors in F. graminearum were shown to have high expression levels during infection on maize,
suggesting a link to fungal virulence . EVs isolated from F. graminearum also have cytotoxic effects when
[55]
infiltrated into barley leaves, but it is unknown if protein effectors, RNAs or metabolites contribute to this
phenomenon .
[24]