Page 76 - Read Online
P. 76
Chen et al. Energy Mater. 2025, 5, 500045 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2024.144 Page 3 of 27
Table 1. Technical characteristics of different water electrolysis technologies [5]
Alkaline water AEM PEM SOEC
electrolysis
Electrolyte KOH/NaOH (1M) KOH/NaOH Solid polymer Solid oxide
(1M) electrolyte
Operating temperature (°C) 70-90 40-60 50-80 700-850
-2
Nominal current density (A·cm ) 0.2-0.8 0.2-2 1-2 0.3-1
Voltage range (V) 1.4-3 1.4-2.0 1.4-2.5 1.0-1.5
Cell pressure (bar) < 30 < 35 < 70 < 10
Efficiency 50%-78% 57%-59% 50%-83% 89%
(laboratory)
Lifetime (thousand hours) 60 > 30 50-80 20
H purity 99.5%-99.9998% 99.9%- 99.9%-99.9999% 99.9%
2
99.9999%
Development Mature R & D Commercialized R & D
Capital costs estimate for large stacks, > 1 MW 270 - 400 > 2,000
(USD/kW )
el
Capital cost range estimate for the entire system, > 10 500-1,000 - 700-1,400 -
MW (USD/kW )
el
[2]
Figure 1. Schematic of clean energy applications. Reproduced with permission from Ref. . Copyright 2023, The Royal Society of
Chemistry.
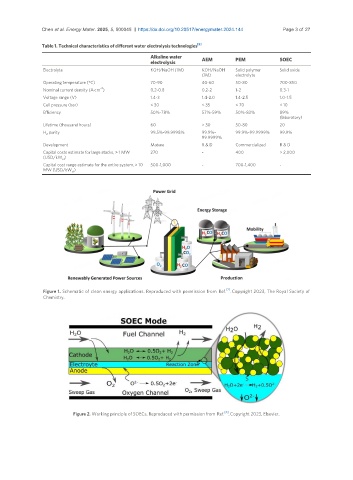
[6]
Figure 2. Working principle of SOECs. Reproduced with permission from Ref. . Copyright 2023, Elsevier.