Page 80 - Read Online
P. 80
Rehman et al. Energy Mater 2024;4:400068 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2024.06 Page 11 of 64
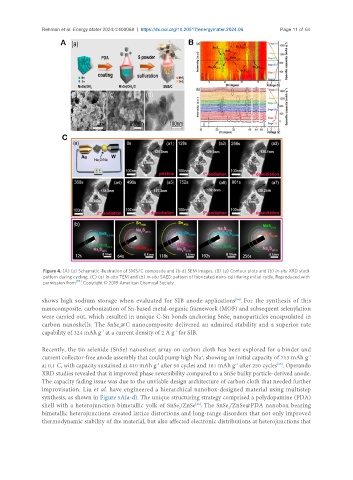
Figure 4. (A) (a) Schematic illustration of SMS/C composite and (b-d) SEM images. (B) (a) Contour plots and (b) in-situ XRD stack
pattern during cycling. (C) (a) In-situ TEM and (b) in-situ SAED pattern of fabricated nano-cell during initial cycle. Reproduced with
permission from [93] . Copyright © 2019 American Chemical Society.
shows high sodium storage when evaluated for SIB anode applications . For the synthesis of this
[94]
nanocomposite, carbonization of Sn-based metal-organic framework (MOF) and subsequent selenylation
were carried out, which resulted in unique C-Sn bonds anchoring SnSe nanoparticles encapsulated in
2
carbon nanoshells. The SnSe @C nanocomposite delivered an admired stability and a superior rate
2
capability of 324 mAh g at a current density of 2 A g for SIB.
-1
-1
Recently, the tin selenide (SnSe) nanosheet array on carbon cloth has been explored for a binder and
+
current collector-free anode assembly that could pump high Na , showing an initial capacity of 713 mAh g
-1
-1
at 0.1 C, with capacity sustained at 410 mAh g after 50 cycles and 161 mAh g after 250 cycles . Operando
-1
[95]
XRD studies revealed that it improved phase reversibility compared to a SnSe bulky particle-derived anode.
The capacity fading issue was due to the unviable design architecture of carbon cloth that needed further
improvisation. Liu et al. have engineered a hierarchical nanobox-designed material using multistep
synthesis, as shown in Figure 5A(a-d). The unique structuring strategy comprised a polydopamine (PDA)
shell with a heterojunction bimetallic yolk of SnSe /ZnSe . The SnSe /ZnSe@PDA nanobox bearing
[96]
2
2
bimetallic heterojunctions created lattice distortions and long-range disorders that not only improved
thermodynamic stability of the material, but also affected electronic distributions at heterojunctions that