Page 131 - Read Online
P. 131
Xiao et al. Energy Mater 2023;3:300007 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2022.84 Page 5 of 13
2+
2+
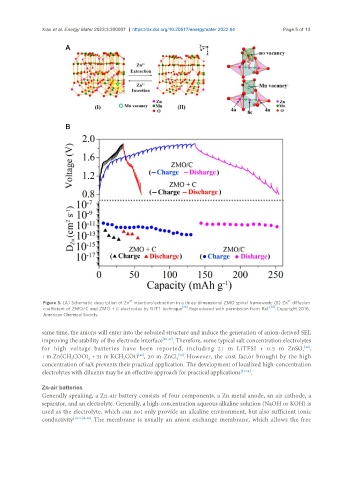
Figure 3. (A) Schematic description of Zn insertion/extraction in a three-dimensional ZMO spinel framework; (B) Zn diffusion
coefficient of ZMO/C and ZMO + C electrodes by GITT technique [38] . Reproduced with permission from Ref. [38] . Copyright 2016,
American Chemical Society.
same time, the anions will enter into the solvated structure and induce the generation of anion-derived SEI,
improving the stability of the electrode interface [45-47] . Therefore, some typical salt concentration electrolytes
for high voltage batteries have been reported, including 21 m LiTFSI + 0.5 m ZnSO ,
[48]
4
1 m Zn(CH COO) + 31 m KCH COO , 30 m ZnCl . However, the cost factor brought by the high
[50]
[49]
3
2
2
3
concentration of salt prevents their practical application. The development of localized high-concentration
electrolytes with diluents may be an effective approach for practical applications [51-54] .
Zn-air batteries
Generally speaking, a Zn-air battery consists of four components, a Zn metal anode, an air cathode, a
separator, and an electrolyte. Generally, a high-concentration aqueous alkaline solution (NaOH or KOH) is
used as the electrolyte, which can not only provide an alkaline environment, but also sufficient ionic
conductivity [10,11,55-58] . The membrane is usually an anion exchange membrane, which allows the free