Page 17 - Read Online
P. 17
Ji et al. Chem Synth 2022;2:17 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cs.2022.27 Page 9 of 11
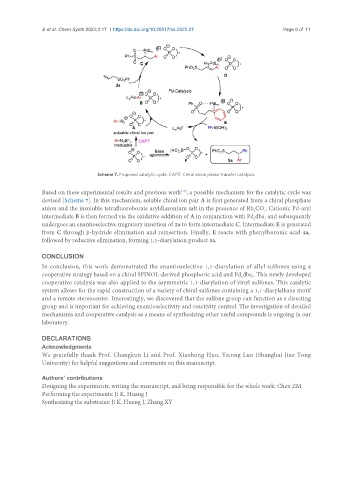
Scheme 7. Proposed catalytic cycle. CAPT: Chiral anion phase-transfer catalysis.
Based on these experimental results and previous work , a possible mechanism for the catalytic cycle was
[10]
devised [Scheme 7]. In this mechanism, soluble chiral ion pair A is first generated from a chiral phosphate
anion and the insoluble tetrafluoroborate aryldiazonium salt in the presence of Rb CO . Cationic Pd-aryl
3
2
intermediate B is then formed via the oxidative addition of A in conjunction with Pd dba and subsequently
2
3
undergoes an enantioselective migratory insertion of 2a to form intermediate C. Intermediate E is generated
from C through β-hydride elimination and reinsertion. Finally, E reacts with phenylboronic acid 4a,
followed by reductive elimination, forming 1,1-diarylation product 5a.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, this work demonstrated the enantioselective 1,1-diarylation of allyl sulfones using a
cooperative strategy based on a chiral SPINOL-derived phosphoric acid and Pd dba . This newly developed
3
2
cooperative catalysis was also applied to the asymmetric 1,1-diarylation of vinyl sulfones. This catalytic
system allows for the rapid construction of a variety of chiral sulfones containing a 1,1-diarylalkane motif
and a remote stereocenter. Interestingly, we discovered that the sulfone group can function as a directing
group and is important for achieving enantioselectivity and reactivity control. The investigation of detailed
mechanisms and cooperative catalysis as a means of synthesizing other useful compounds is ongoing in our
laboratory.
DECLARATIONS
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank Prof. Changkun Li and Prof. Xiaohong Huo, Yicong Luo (Shanghai Jiao Tong
University) for helpful suggestions and comments on this manuscript.
Authors’ contributions
Designing the experiments, writing the manuscript, and being responsible for the whole work: Chen ZM
Performing the experiments: Ji K, Huang J
Synthesizing the substrates: Ji K, Huang J, Zhang XY