Page 44 - Read Online
P. 44
Cui et al. Complex Eng Syst 2023;3:3 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ces.2022.57 Page 3 of 15
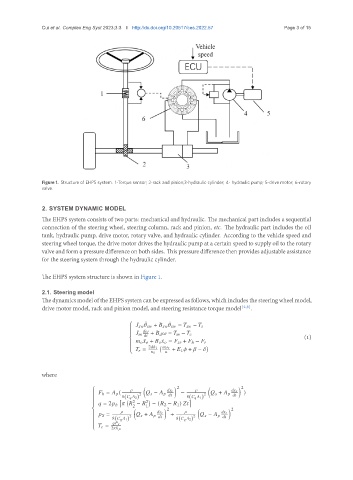
Figure 1. Structure of EHPS system. 1-Torque sensor; 2-rack and pinion;3-hydraulic cylinder; 4- hydraulic pump; 5-drive motor; 6-rotary
valve.
2. SYSTEM DYNAMIC MODEL
The EHPS system consists of two parts: mechanical and hydraulic. The mechanical part includes a sequential
connection of the steering wheel, steering column, rack and pinion, etc. The hydraulic part includes the oil
tank, hydraulic pump, drive motor, rotary valve, and hydraulic cylinder. According to the vehicle speed and
steering wheel torque, the drive motor drives the hydraulic pump at a certain speed to supply oil to the rotary
valve and form a pressure difference on both sides. This pressure difference then provides adjustable assistance
for the steering system through the hydraulic cylinder.
The EHPS system structure is shown in Figure 1.
2.1. Steering model
The dynamics model of the EHPS system can be expressed as follows, which includes the steering wheel model,
drive motor model, rack and pinion model, and steering resistance torque model [2,8] .
¥ ¤
+ = −
(1)
+ = −
¥ + ¤ = + ℎ −
2 1
= + 1 + −
1
where
2 2
ℎ = ( − − + )
2 2
8( 2) 8( 1)
2 2
= 2 − − ( 2 − 1 )
2 1
2 2
=
+
2 + 2 −
8( 1) 8( 2)
=
2