Page 44 - Read Online
P. 44
Bijnsdorp et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2021;4:719-27 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2021.21 Page 723
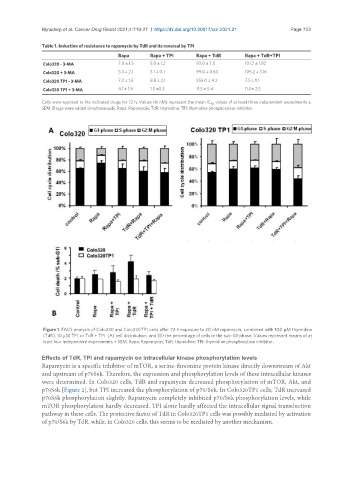
Table 1. Induction of resistance to rapamycin by TdR and its reversal by TPI
Rapa Rapa + TPI Rapa + TdR Rapa + TdR+TPI
Colo320 - 3-MA 7.0 ± 1.5 5.0 ± 1.2 93.0 ± 7.0 101.7 ± 1.82
Colo320 + 3-MA 5.3 ± 2.1 3.1 ± 0.1 99.0 ± 0.63 105.2 ± 3.16
Colo320 TP1 - 3-MA 7.2 ± 1.5 8.8 ± 2.1 355.0 ± 4.2 7.5 ± 1.1
Colo320 TP1 + 3-MA 4.1 ± 1.9 1.5 ±0.3 11.5 ± 5.4 11.1 ± 2.5
Cells were exposed to the indicated drugs for 72 h. Values (in nM) represent the mean IC values of at least three independent experiments ±
50
SEM. Drugs were added simultaneously. Rapa: Rapamycin; TdR: thymidine; TPI: thymidine phosphorylase inhibitor.
Figure 1. FACS analysis of Colo230 and Colo320TP1 cells after 72 h exposure to 20 nM rapamycin, combined with 100 µM thymidine
(TdR), 10 µM TPI, or TdR + TPI: (A) cell distribution; and (B) the percentage of cells in the sub-G1-phase. Values represent means of at
least four independent experiments ± SEM. Rapa: Rapamycin; TdR: thymidine; TPI: thymidine phosphorylase inhibitor.
Effects of TdR, TPI and rapamycin on intracellular kinase phosphorylation levels
Rapamycin is a specific inhibitor of mTOR, a serine-threonine protein kinase directly downstream of Akt
and upstream of p70S6k. Therefore, the expression and phosphorylation levels of these intracellular kinases
were determined. In Colo320 cells, TdR and rapamycin decreased phosphorylation of mTOR, Akt, and
p70S6k [Figure 2], but TPI increased the phosphorylation of p70/S6k. In Colo320TP1 cells, TdR increased
p70S6k phosphorylation slightly. Rapamycin completely inhibited p70/S6k phosphorylation levels, while
mTOR phosphorylation hardly decreased. TPI alone hardly affected the intracellular signal transduction
pathway in these cells. The protective factor of TdR in Colo320TP1 cells was possibly mediated by activation
of p70/S6k by TdR, while, in Colo320 cells, this seems to be mediated by another mechanism.