Page 46 - Read Online
P. 46
Page 156 Lotz et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2020;3:149-60 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2019.114
A
B C
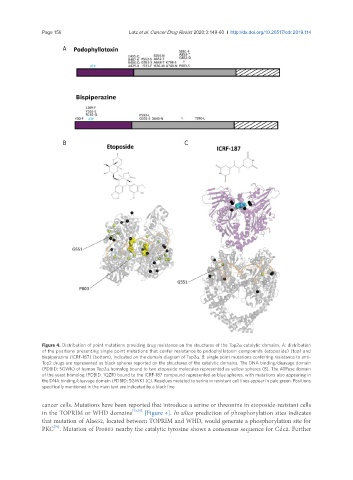
Figure 4. Distribution of point mutations providing drug resistance on the structures of the Top2a catalytic domains. A: distribution
of the positions presenting single point mutations that confer resistance to podophyllotoxin compounds (etoposide) (top) and
bispiperazine (ICRF-187) (bottom), indicated on the domain diagram of Top2a. B: single point mutations conferring resistance to anti-
Top2 drugs are represented as black spheres reported on the structures of the catalytic domains. The DNA binding/cleavage domain
(PDBID: 5GWK) of human Top2a homolog bound to two etoposide molecules represented as yellow spheres (B). The ATPase domain
of the yeast homolog (PDBID: 1QZR) bound to the ICRF-187 compound represented as blue spheres, with mutations also appearing in
the DNA binding/cleavage domain (PDBID: 5GWK) (C). Residues mutated to serine in resistant cell lines appear in pale green. Positions
specifically mentioned in the main text are indicated by a black line
cancer cells. Mutations have been reported that introduce a serine or threonine in etoposide-resistant cells
in the TOPRIM or WHD domains [73,75] [Figure 4]. In silico prediction of phosphorylation sites indicates
that mutation of Ala652, located between TOPRIM and WHD, would generate a phosphorylation site for
PKC . Mutation of Pro803 nearby the catalytic tyrosine shows a consensus sequence for Cdc2. Further
[76]