Page 124 - Read Online
P. 124
Page 308 Ponnusamy et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:297-312 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2018.11
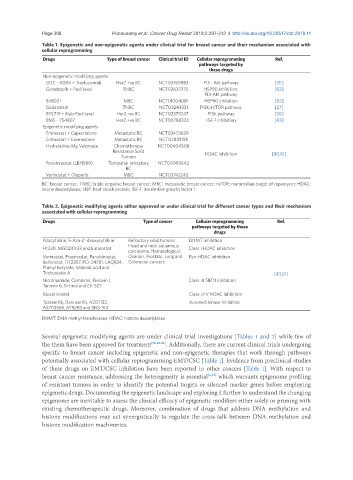
Table 1. Epigenetic and non-epigenetic agents under clinical trial for breast cancer and their mechanism associated with
cellular reprogramming
Drugs Type of breast cancer Clinical trial ID Cellular reprogramming Ref.
pathways targeted by
these drugs
Non-epigenetic modifying agents
GDC - 0084 + Trastuzumab Her2 +ve BC NCT03765983 PI3 - Akt pathway [30]
Ganetespib + Paclitaxel TNBC NCT02637375 HSP90 inhibition; [82]
PI3-Akt pathway
BIIB021 MBC NCT01004081 HSP90 inhibition [82]
Gedatolisib TNBC NCT03243331 PI3K/mTOR pathway [27]
BYL719 + Nab-Paclitaxel Her2 -ve BC NCT02379247 PI3K pathway [30]
BMS - 754807 Her2 +ve BC NCT00788333 IGF-1 inhibition [83]
Epigenetic modifying agents
Entinostat + Capecitabine Metastatic BC NCT03473639
Entinostat + Exemestane Metastatic BC NCT02833155
Hydralazine-Mg Valproate Chemotherapy NCT00404508
Resistance Solid HDAC inhibition [80,81]
Tumors
Panobinostat (LBH589) Tamoxifen refractory NCT00993642
BC
Vorinostat + Olaparib MBC NCT03742245
BC: breast cancer; TNBC: triple negative breast cancer; MBC: metastatic breast cancer; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; HDAC:
istone deacetylases; HSP: heat shock protein; IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor 1
Table 2. Epigenetic modifying agents either approved or under clinical trial for different cancer types and their mechanism
associated with cellular reprogramming
Drugs Type of cancer Cellular reprogramming Ref.
pathways targeted by these
drugs
Azacytidine, 5-Aza-2’-deoxycytidine Refractory solid tumors; DNMT inhibition
Head and neck squamous
FK228, MGCD0103 and Entinostat Class I HDAC inhibition
carcinoma; Hematological;
Vorinostat, Pracinostat, Panobinostat, Ovarian, Prostate, Lung and Pan-HDAC inhibition
Belinostat, ITF2357, PCI-24781, LAQ824, Colorectal cancers
Phenyl butyrate, Valproic acid and
Trichostatin A [80,81]
Nicotinamide, Cambinol, Tenovin 1, Class III SIRT1 inhibition
Tenovin 6, Sirtinol and EX-527
Mocetinostat Class I/IV HDAC inhibition
Tozasertib, Danusertib, AZD1152, Aurora-B kinase inhibition
AS703569, AT9283 and SNS-314
DNMT: DNA methyl transferases; HDAC: histone deacetylases
Several epigenetic modifying agents are under clinical trial investigations [Tables 1 and 2] while few of
the them have been approved for treatment [52,80,81] . Additionally, there are current clinical trials undergoing
specific to breast cancer including epigenetic and non-epigenetic therapies that work through pathways
potentially associated with cellular reprogramming-EMT/CSC [Table 1]. Evidence from preclinical studies
of these drugs on EMT/CSC inhibition have been reported in other cancers [Table 1]. With respect to
breast cancer resistance, addressing the heterogeneity is essential [3,23] which warrants epigenome profiling
of resistant tumors in order to identify the potential targets or silenced marker genes before employing
epigenetic drugs. Documenting the epigenetic landscape and exploring it further to understand the changing
epigenome are inevitable to assess the clinical efficacy of epigenetic modifiers either solely or priming with
existing chemotherapeutic drugs. Moreover, combination of drugs that address DNA methylation and
histone modifications may act synergistically to regulate the cross-talk between DNA methylation and
histone modification machineries.