Page 188 - Read Online
P. 188
Page 684 Alonso-Peña et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:680-709 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2019.006
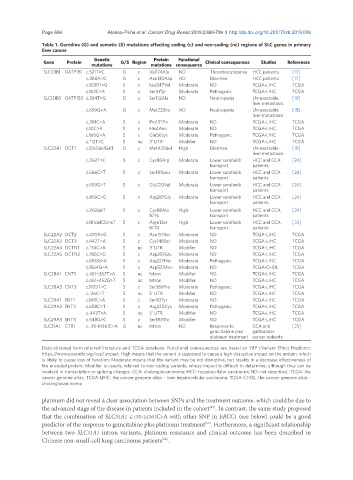
Table 1. Germline (G) and somatic (S) mutations affecting coding (c) and non-coding (nc) regions of SLC genes in primary
liver cancer
Genetic Protein Functional
Gene Protein G/S Region Clinical consequences Studies References
mutations mutations consequence
SLCO1B1 OATP1B1 c.521T>C G c Val174Ala ND Thrombocytopenia HCC patients [17]
c.388A>G G c Asn130Asp ND Diarrhea HCC patients [17]
c.1039T>G S c Leu347Val Moderate ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.152C>A S c Ser51Tyr Moderate Pathogenic TCGA-LIHC TCGA
SLCO1B3 OATP1B3 c.334T>G G c Ser112Ala ND Neutropenia Unresectable [18]
liver metastasis
c.699G>A G c Met233Ile ND Neutropenia Unresectable [18]
liver metastasis
c.391C>A S c Pro131Thr Moderate ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.10C>A S c His4Asn Moderate ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.166G>A S c Glu56Lys Moderate Pathogenic TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.*12T>C S nc 3‘ UTR Modifier ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
SLC22A1 OCT1 c.1260delGAT G c Met420del High Diarrhea Unresectable [18]
liver metastasis
c.262T>C S c Cys88Arg Moderate Lower sorafenib HCC and CCA [24]
transport patients
c.566C>T S c Ser189Leu Moderate Lower sorafenib HCC and CCA [24]
transport patients
c.659G>T S c Gly220Val Moderate Lower sorafenib HCC and CCA [24]
transport patients
c.859C>G S c Arg287Gly Moderate Lower sorafenib HCC and CCA [24]
transport patients
c.262delT S c Cys88Ala High Lower sorafenib HCC and CCA [24]
fs*16 transport patients
c.181delCGinsT S c Arg61Ser High Lower sorafenib HCC and CCA [24]
fs*10 transport patients
SLC22A2 OCT2 c.470A>G S c Asn157Ser Moderate ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
SLC22A3 OCT3 c.442T>A S c Cys148Ser Moderate ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
SLC22A4 OCTN1 c.*34C>A S nc 3‘ UTR Modifier ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
SLC22A5 OCTN2 c.765C>G S c Asp255Glu Moderate ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.680G>A S c Arg227His Moderate Pathogenic TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.1564G>A S c Asp522Asn Moderate ND TCGA-CHOL TCGA
SLC28A1 CNT1 c.461+367T>A S nc Intron Modifier ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.461+452G>T S nc Intron Modifier ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
SLC28A3 CNT3 c.1105T>C S c Ser369Pro Moderate Pathogenic TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.-26C>T S nc 5‘ UTR Modifier ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
SLC29A1 ENT1 c.149C>A S c Ser50Tyr Moderate ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
SLC29A2 ENT2 c.658C>T S c Arg220Cys Moderate Pathogenic TCGA-LIHC TCGA
c.-143T>A S nc 5‘ UTR Modifier ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
SLC29A3 ENT3 c.548G>C S c Ser183Thr Modifier ND TCGA-LIHC TCGA
SLC31A1 CTR1 c.-35-14361C>A G nc Intron ND Response to CCA and [25]
gemcitabine plus gallbladder
platinum treatment cancer patients
Data obtained from referred literature and TCGA database. Functional consequences are based on VEP (Variant Effect Predictor;
https://www.ensembl.org/vep) impact: High means that the variant is supposed to cause a high disruptive impact on the protein, which
is likely to cause loss of function; Moderate means that the variant may be not disruptive, but results in a decrease effectiveness of
the encoded protein; Modifier is usually referred to non-coding variants, whose impact is difficult to determine, although they can be
involved in transcription or splicing changes. CCA: cholangiocarcinoma; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; ND: not described; TCGA: the
cancer genome atlas; TCGA-LIHC: the cancer genome atlas - liver hepatocellular carcinoma; TCGA-CHOL: the cancer genome atlas -
cholangiocarcinoma
platinum did not reveal a clear association between SNPs and the treatment outcome, which could be due to
the advanced stage of the disease in patients included in the cohort . In contrast, the same study proposed
[25]
that the combination of SLC31A1 c.-35-14361C>A with other SNP in ERCC1 (see below) could be a good
predictor of the response to gemcitabine plus platinum treatment . Furthermore, a significant relationship
[25]
between two SLC31A1 intron variants, platinum resistance and clinical outcome has been described in
Chinese non-small-cell lung carcinoma patients .
[26]