Page 51 - Read Online
P. 51
Page 150 Sendino et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2018;1:139-63 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2018.09
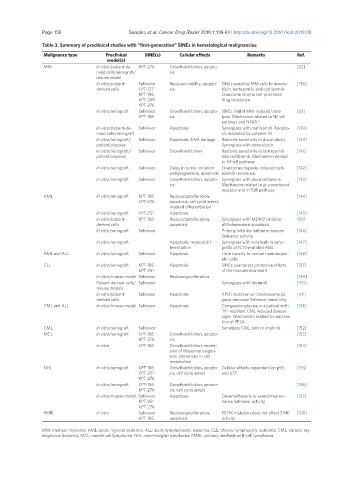
Table 3. Summary of preclinical studies with “first-generation” SINEs in hematological malignancies
Malignancy type Preclinical SINE(s) Cellular effects Remarks Ref.
model(s)
MM In vitro/patient-de- KPT-276 Growth inhibition, apopto- [82]
rived cells/xenograft/ sis
mouse model
In vitro/patient- Selinexor Reduced viability, apopto- SINEs sensitize MM cells to doxoru- [138]
derived cells KPT-127 sis bicin, bortezomib, and carfilzomib.
KPT-185 Overcome stroma cell-promoted
KPT-249 drug resistance
KPT-276
In vitro/xenograft Selinexor Growth inhibition, apopto- SINEs inhibit MM-induced bone [83]
KPT-185 sis lysis. Mechanism related to NF-κB
pathway and NFATc1
In vitro/patient-de- Selinexor Apoptosis Synergizes with carfilzomib. Apopto- [139]
rived cells/xenograft sis mediated by caspase 10
In vitro/xenograft/ Selinexor Apoptosis, DNA damage Restores sensitivity to doxorubicin. [140]
patient biopsies Synergizes with doxorubicin
In vitro/xenograft/ Selinexor Growth inhibition Restores sensitivity to bortezomib [141]
patient biopsies and carfilzomib. Mechanism related
to NF-κB pathway
In vitro/xenograft Selinexor Delay in tumor initiation Overcomes hypoxia-induced bort- [142]
and progression, apoptosis ezomib resistance
In vitro/xenograft Selinexor Growth inhibition, apopto- Synergizes with dexamethasone. [143]
sis Mechanism related to glucocorticoid
receptor and mTOR pathway
AML In vitro/xenograft KPT-185 Reduced proliferation, [144]
KPT-276 apoptosis, cell cycle arrest,
myeloid differentiation
In vitro/xenograft KPT-251 Apoptosis [145]
In vitro/patient- KPT-185 Reduced proliferation, Synergizes with MDM2 inhibitor. [80]
derived cells apoptosis p53-dependent apoptosis
In vitro/xenograft Selinexor Priming with decitabine enhances [146]
Selinexor activity
In vitro/xenograft Apoptosis, myeloid dif- Synergizes with sorafenib in xeno- [147]
ferentiation grafts of FLT3-mutated AML
AML and ALL In vitro/xenograft Selinexor Apoptosis Little toxicity to normal haematopoi- [148]
etic cells
CLL In vitro/xenograft KPT-185 Apoptosis SINEs counteract protective effects [137]
KPT-251 of the microenvironment
In vitro/mouse model Selinexor Reduced proliferation [149]
Patient-derived cells/ Selinexor Synergizes with ibrutinib [150]
mouse models
In vitro/patient- Selinexor Apoptosis XPO1 mutation or chromosome 2p [101]
derived cells gains decrease Selinexor sensitivity
CML and ALL In vitro/mouse model Selinexor Apoptosis Compassionate use in a patient with [151]
TKI-resistant CML reduced disease
signs. Mechanism related to reactiva-
tion of PP2A
CML In vitro/xenograft Selinexor Sensitizes CML cells to imatinib [152]
MCL In vitro/xenograft KPT-185 Growth inhibition, apopto- [153]
KPT-276 sis
In vitro KPT-185 Growth inhibition, repres- [154]
sion of ribosomal biogen-
esis, alterations in cell
metabolism
NHL In vitro/xenograft KPT-185 Growth inhibition, apopto- Cellular effects dependent on p53 [155]
KPT-251 sis, cell cycle arrest and p73
KPT-276
In vitro/xenograft KPT-185 Growth inhibition, apopto- [156]
KPT-276 sis, cell cycle arrest
In vitro/mouse model Selinexor Apoptosis Dexamethasone or everolimus en- [157]
KPT-251 hance Selinexor activity
KPT-276
PMBL In vitro Selinexor Reduced proliferation, E571K mutation does not affect SINE [100]
KPT-185 apoptosis activity
MM: multiple myeloma; AML: acute myeloid leukemia; ALL: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; CLL: chronic lymphocytic leukemia; CML: chronic my-
elogenous leukemia; MCL: mantle cell lymphoma; NHL: non-Hodgkin lymphoma; PMBL: primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma