Page 82 - Read Online
P. 82
Page 468 Wang et al. Art Int Surg. 2025;5:465-75 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2025.03
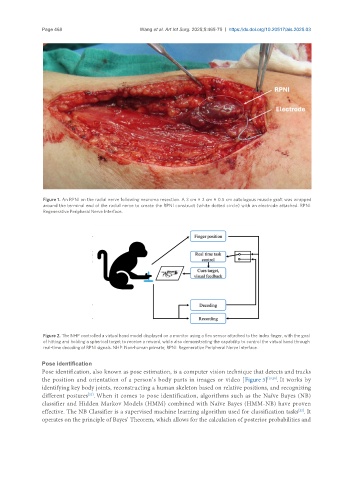
Figure 1. An RPNI on the radial nerve following neuroma resection. A 3 cm × 2 cm × 0.5 cm autologous muscle graft was wrapped
around the terminal end of the radial nerve to create the RPNI construct (white dotted circle) with an electrode attached. RPNI:
Regenerative Peripheral Nerve Interface.
Figure 2. The NHP controlled a virtual hand model displayed on a monitor using a flex sensor attached to the index finger, with the goal
of hitting and holding a spherical target to receive a reward, while also demonstrating the capability to control the virtual hand through
real-time decoding of RPNI signals. NHP: Non-human primate; RPNI: Regenerative Peripheral Nerve Interface.
Pose identification
Pose identification, also known as pose estimation, is a computer vision technique that detects and tracks
the position and orientation of a person’s body parts in images or video [Figure 3] [19,20] . It works by
identifying key body joints, reconstructing a human skeleton based on relative positions, and recognizing
different postures . When it comes to pose identification, algorithms such as the Naïve Bayes (NB)
[21]
classifier and Hidden Markov Models (HMM) combined with Naïve Bayes (HMM-NB) have proven
effective. The NB Classifier is a supervised machine learning algorithm used for classification tasks . It
[22]
operates on the principle of Bayes’ Theorem, which allows for the calculation of posterior probabilities and