Page 13 - Read Online
P. 13
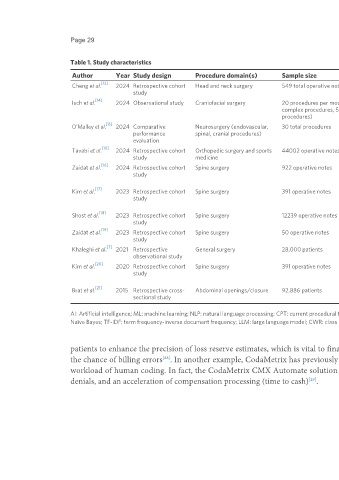
Page 29 Landau et al. Art Int Surg. 2025;5:24-35 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2024.78
Table 1. Study characteristics
Author Year Study design Procedure domain(s) Sample size AI/ML/NLP tested CPT codes assessed
[13]
Cheng et al. 2024 Retrospective cohort Head and neck surgery 549 total operative notes ML (bagging DT, RF DT, SVM, LR, NB), NLP 6 total CPT codes (30520, 31255, 31267,
study (count vectorizer, TF-IDF, Word2Vec) 31276, 31288, and 61580)
[14]
Isch et al. 2024 Observational study Craniofacial surgery 20 procedures per model (15 LLM (Bard, Perplexity.AI, BingAI, ChatGPT CPT codes for craniofacial surgery
complex procedures, 5 simple 3.5, ChatGPT 4.0) procedures (unspecified)
procedures)
[15]
O’Malley et al. 2024 Comparative Neurosurgery (endovascular, 30 total procedures LLM [Bard, Perplexity.AI, BingAI, ChatGPT Various CPT codes for each procedure,
performance spinal, cranial procedures) 3.5, ChatGPT 4.0, Google Search (control)] depending on the number of actions
evaluation performed
[10]
Tavabi et al. 2024 Retrospective cohort Orthopedic surgery and sports 44002 operative notes NLP (TF-IDF, Doc2Vec, Clinical-BERT), ML 20100-29999
study medicine (SVM with RBF kernel)
[16]
Zaidat et al. 2024 Retrospective cohort Spine surgery 922 operative notes NLP [XLNet (generalized autoregressive 24 CPT codes (analysis limited to codes
study pretraining method)] with at least 50 appearances in operative
notes)
[17]
Kim et al. 2023 Retrospective cohort Spine surgery 391 operative notes Deep learning (bidirectional long short-term 15 CPT codes (analysis limited to codes
study memory), ML (RF), NLP with at least 50 appearances in operative
notes)
[18]
Shost et al. 2023 Retrospective cohort Spine surgery 12239 operative notes NLP (TensorFlow open-source package for CPT codes specific to 7 types of cervical
study Python) spine surgery
[19]
Zaidat et al. 2023 Retrospective cohort Spine surgery 50 operative notes LLM (ChatGPT-4), ML Various (most frequent codes include CPT
study 22551, 22552, 20931, 20936)
[7]
Khaleghi et al. 2021 Retrospective General surgery 28,000 patients RF classifier, CWR, TFIDF, levenshtein 891 unique CPT codes in the full dataset
observational study distance
[20]
Kim et al. 2020 Retrospective cohort Spine surgery 391 operative notes Bidirectional long short-term memory 36 CPT codes with high performance
study network with attention (deep learning NLP
algorithm)
[21]
Brat et al. 2015 Retrospective cross- Abdominal openings/closure 92,886 patients Word vector algorithm, GBT model Quantity unspecified
sectional study
AI: Artificial intelligence; ML: machine learning; NLP: natural language processing; CPT: current procedural terminology; DT: decision tree; RF: random forest; SVM: support vector machine; LR: logistic regression; NB:
Naïve Bayes; TF-IDF: term frequency-inverse document frequency; LLM: large language model; CWR: class weight recalculation; GBT: gradient boosted trees.
patients to enhance the precision of loss reserve estimates, which is vital to financial reporting by accelerating the timeframe for reimbursement and lowering
[28]
the chance of billing errors . In another example, CodaMetrix has previously been integrated into Epic systems, combining AI methodologies to reduce the
workload of human coding. In fact, the CodaMetrix CMX Automate solution boasts a remarkable 60% reduction in coding costs, a 70% reduction in claims
denials, and an acceleration of compensation processing (time to cash) .
[29]