Page 35 - Read Online
P. 35
Page 216 Boutros et al. Art Int Surg 2022;2:213-23 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2022.32
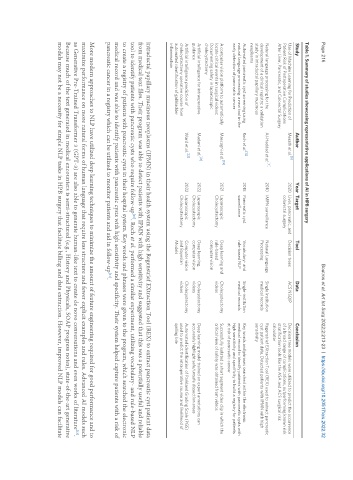
Table 1. Summary of studies showcasing representative applications of AI in HPB surgery
Study Author Year Target Tool Data Conclusion
Use of Machine Learning for Prediction of Merath et al. [9] 2020 Liver, pancreatic, and Decision trees ACS NSQIP Decision tree models were utilized to predict the occurrence
Patient Risk of Postoperative Complications colorectal surgery of a broad range of complications, outperforming known risk
After Liver, Pancreatic, and Colorectal Surgery stratification tools like the ASA and ACS surgical risk
calculator
[11]
Natural language processing for the Al-Haddad et al. 2010 IMPN surveillance Natural Language Single institution Regenstrief EXtraction Tool (REX) used to extract pancreatic
development of a clinical registry: a validation Processing medical records cyst patient data. Detected patients with IPMN with high
study in intraductal papillary mucinous sensitivity
neoplasms
[12]
Automated pancreatic cyst screening using Roch et al. 2015 Pancreatic cyst Vocabulary- and Single-institution Key words and phrases searched within the electronic
natural language processing: a new tool in the surveillance rule-based NLP medical records medical record to identify patients with pancreatic cysts with
early detection of pancreatic cancer high sensitivity and specificity to build a registry for patients
at risk of pancreatic cancer
[19]
A computer vision platform to automatically Mascagni et al. 2021 Laparoscopic Deep learning and Cholecystectomy Successfully isolated a short segment video clip in which the
locate critical events in surgical videos: Cholecystectomy rule-based videos critical view of safety was obtained from videos
Documenting safety in laparoscopic computer vision
cholecystectomy
Artificial intelligence for intraoperative Madani et al. [21] 2022 Laparoscopic Deep learning, Cholecystectomy Deep learning model trained on expert annotations can
guidance Cholecystectomy computer vision videos accurately highlight safe/unsafe dissection areas
Artificial intelligence prediction of Ward et al. [22] 2022 Laparoscopic Computer vision Cholecystectomy Automated identification of Parkland Grading Scale (PGS)
cholecystectomy operative course from Cholecystectomy and Bayesian videos used to predict the intraoperative course and likelihood of
automated identification of gallbladder Models spilling bile
inflammation
intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN) in their health system using the Regenstrief EXtraction Tool (REX) to extract pancreatic cyst patient data
from medical text files. Their program was able to detect patients with IPMN with high sensitivity and suggested that this was a potentially useful and reliable
tool to identify patients with pancreatic cysts who require follow-up . Roch et al. performed a similar experiment, utilizing vocabulary- and rule-based NLP
[10]
to create a registry of patients with pancreatic cysts in their hospital system. Key words and phrases were given to the program, which searched the electronic
medical record and was able to identify patients with pancreatic cysts with high sensitivity and specificity. Their system helped capture patients with a risk of
pancreatic cancer in a registry which can be utilized to monitor patients and aid in follow-up .
[11]
More modern approaches to NLP have utilized deep learning techniques to minimize the amount of feature engineering required for good performance and to
maximize performance on more natural forms of human language that require less structure and fewer explicit examples and rules. Advanced AI models such
[12]
as Generative Pre-Trained Transformer 3 (GPT-3) are also able to generate human-like text to create de novo conversations and even works of literature .
Because much of the text generated in medical encounters is semi-structured (e.g., History and Physicals, SOAP progress notes), state-of-the-art generative
models may not be a necessity for simple NLP tasks in HPB surgery that facilitate billing and data extraction. However, improved NLP models can facilitate