Page 129 - Read Online
P. 129
Page 169 De Robertis et al. Art Int Surg 2023;3:166-79 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2023.18
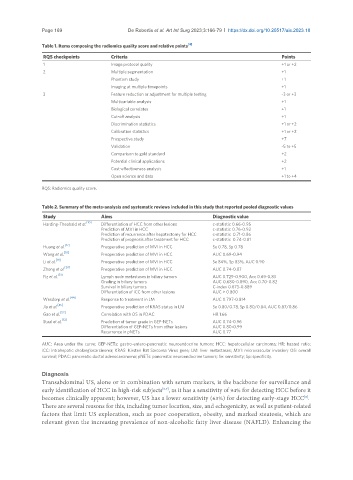
Table 1. Items composing the radiomics quality score and relative points [4]
RQS checkpoints Criteria Points
1 Image protocol quality +1 or +2
2 Multiple segmentation +1
Phantom study +1
Imaging at multiple timepoints +1
3 Feature reduction or adjustment for multiple testing -3 or +3
Multivariable analysis +1
Biological correlates +1
Cut-off analysis +1
Discrimination statistics +1 or +2
Calibration statistics +1 or +2
Prospective study +7
Validation -5 to +5
Comparison to gold standard +2
Potential clinical applications +2
Cost-effectiveness analysis +1
Open science and data +1 to +4
RQS: Radiomics quality score.
Table 2. Summary of the meta-analysis and systematic reviews included in this study that reported pooled diagnostic values
Study Aims Diagnostic value
Harding-Theobald et al. [10] Differentiation of HCC from other lesions c-statistic 0.66-0.95
Prediction of MVI in HCC c-statistic 0.76-0.92
Prediction of recurrence after hepatectomy for HCC c-statistic 0.71-0.86
Prediction of prognosis after treatment for HCC c-statistic 0.74-0.81
[17]
Huang et al. Preoperative prediction of MVI in HCC Se 0.78, Sp 0.78
[18]
Wang et al. Preoperative prediction of MVI in HCC AUC 0.69-0.94
[19]
Li et al. Preoperative prediction of MVI in HCC Se 84%, Sp 83%, AUC 0.90
Zhong et al. [20] Preoperative prediction of MVI in HCC AUC 0.74-0.87
[31]
Fiz et al. Lymph node metastases in biliary tumors AUC 0.729-0.900, Acc 0.69-0.83
Grading in biliary tumors AUC 0.680-0.890, Acc 0.70-0.82
Survival in biliary tumors C-index 0.673-0.889
Differentiation of iCC from other lesions AUC > 0.800
[44]
Wesdorp et al. Response to treatment in LM AUC 0.797-0.814
Jia et al. [45] Preoperative prediction of KRAS status in LM Se 0.80/0.78, Sp 0.80/0.84, AUC 0.87/0.86
[52]
Gao et al. Correlation with OS in PDAC HR 1.66
[53]
Staal et al. Prediction of tumor grade in GEP-NETs AUC 0.74-0.96
Differentiation of GEP-NETs from other lesions AUC 0.80-0.99
Recurrence in pNETs AUC 0.77
AUC: Area under the curve; GEP-NETs: gastro-entero-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; HR: hazard ratio;
iCC: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; KRAS: Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Virus gene; LM: liver metastases; MVI: microvascular invasion; OS: overall
survival; PDAC: pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; pNETs: pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors; Se: sensitivity; Sp: specificity.
Diagnosis
Transabdominal US, alone or in combination with serum markers, is the backbone for surveillance and
early identification of HCC in high-risk subjects , as it has a sensitivity of 94% for detecting HCC before it
[6,7]
[8]
becomes clinically apparent; however, US has a lower sensitivity (63%) for detecting early-stage HCC .
There are several reasons for this, including tumor location, size, and echogenicity, as well as patient-related
factors that limit US exploration, such as poor cooperation, obesity, and marked steatosis, which are
relevant given the increasing prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Enhancing the