Page 57 - Read Online
P. 57
Persico et al. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2023;2:xx https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2023.08 Page 13 of 21
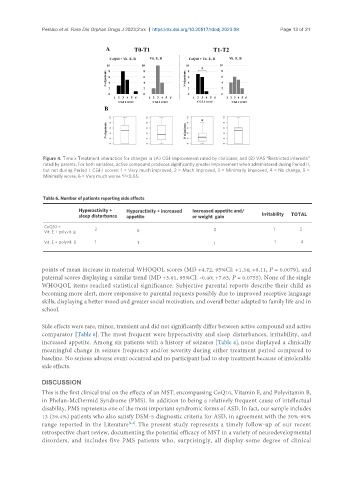
Figure 4. Time x Treatment interaction for changes in (A) CGI-Improvement rated by clinicians; and (B) VAS “Restricted interests”
rated by parents. For both variables, active compound produces significantly greater improvement when administered during Period II,
but not during Period I. CGI-I scores: 1 = Very much improved, 2 = Much improved, 3 = Minimally improved, 4 = No change, 5 =
Minimally worse, 6 = Very much worse.*P<0.05.
Table 6. Number of patients reporting side effects
Hyperactivity + Hyperactivity + increased Increased appetite and/
sleep disturbance appetite or weight gain Irritability TOTAL
CoQ10 +
2 0 1 3
Vit. E + polyvit. B 0
Vit. E + polyvit. B 1 1 1 1 4
points of mean increase in maternal WHOQOL scores (MD +4.72, 95%CI: +1.34; +8.11, P = 0.0079), and
paternal scores displaying a similar trend (MD +3.61, 95%CI: -0.40; +7.63, P = 0.0755). None of the single
WHOQOL items reached statistical significance. Subjective parental reports describe their child as
becoming more alert, more responsive to parental requests possibly due to improved receptive language
skills, displaying a better mood and greater social motivation, and overall better adapted to family life and in
school.
Side effects were rare, minor, transient and did not significantly differ between active compound and active
comparator [Table 6]. The most frequent were hyperactivity and sleep disturbances, irritability, and
increased appetite. Among six patients with a history of seizures [Table 4], none displayed a clinically
meaningful change in seizure frequency and/or severity during either treatment period compared to
baseline. No serious adverse event occurred and no participant had to stop treatment because of intolerable
side effects.
DISCUSSION
This is the first clinical trial on the effects of an MST, encompassing CoQ10, Vitamin E, and Polyvitamin B,
in Phelan-McDermid Syndrome (PMS). In addition to being a relatively frequent cause of intellectual
disability, PMS represents one of the most important syndromic forms of ASD. In fact, our sample includes
13 (39.4%) patients who also satisfy DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for ASD, in agreement with the 30%-80%
[6-8]
range reported in the Literature . The present study represents a timely follow-up of our recent
retrospective chart review, documenting the potential efficacy of MST in a variety of neurodevelopmental
disorders, and includes five PMS patients who, surprisingly, all display some degree of clinical