Page 56 - Read Online
P. 56
Page 12 of 21 Persico et al. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2023;2:xx https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2023.08
Table 5. Primary outcome measures reaching nominal significance, indicating (A) greater improvement with active compound
[CoQ10 + Vit. E + polyvit. B] vs. active comparator [Vit. E + polyvit. B], or (B) Time × Treatment interactions with active compound
displaying greater efficacy when administered during period II, but not during period I (also see Figure 4, A and B).
Subscale MD or cOR 95% CI Nominal P-value
A VABS Motor Skills +6.81 +1.89 +11.72 0.0147
VAS Stereotyped or repetitive motor movements (rated by parents) -0.79 -1.45 -0.13 0.0198
VAS Stereotyped or repetitive motor movements (rated by clinicians) -0.97 -2.06 0.12 0.0770
VAS Enjoyment in shared play (rated by parents) -0.54 -0.99 -0.09 0.0199
B VAS Restricted Interest (rated by parents) - T1 +0.42 -0.18 +1.01 0.1701
- T2 -1.40 -2,76 -0.04 0.0434
CGI-Improvement - T1 +0.78 +0.21 +2.94 0.7150
- T2 +4.55 +1.12 +20.00 0.0336
MD: mean difference; cOR: cumulative odds ratio.
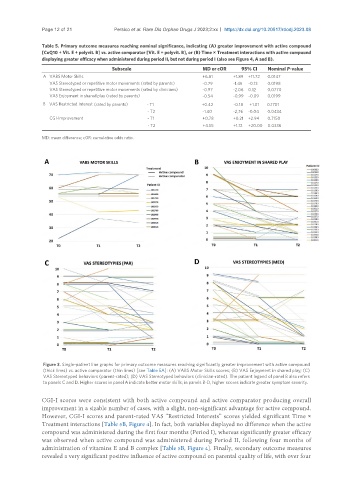
Figure 3. Single-patient line graphs for primary outcome measures reaching significantly greater improvement with active compound
(thick lines) vs. active comparator (thin lines) [see Table 5A]: (A) VABS Motor Skills scores; (B) VAS Enjoyment in shared play; (C)
VAS Stereotyped behaviors (parent-rated); (D) VAS Stereotyped behaviors (clinician-rated). The patient legend of panel B also refers
to panels C and D. Higher scores in panel A indicate better motor skills; in panels B-D, higher scores indicate greater symptom severity.
CGI-I scores were consistent with both active compound and active comparator producing overall
improvement in a sizable number of cases, with a slight, non-significant advantage for active compound.
However, CGI-I scores and parent-rated VAS “Restricted Interests” scores yielded significant Time ×
Treatment interactions [Table 5B, Figure 4]. In fact, both variables displayed no difference when the active
compound was administered during the first four months (Period I), whereas significantly greater efficacy
was observed when active compound was administered during Period II, following four months of
administration of vitamins E and B complex [Table 5B, Figure 4]. Finally, secondary outcome measures
revealed a very significant positive influence of active compound on parental quality of life, with over four