Page 42 - Read Online
P. 42
Fetro. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2023;2:7 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2023.06 Page 5 of 16
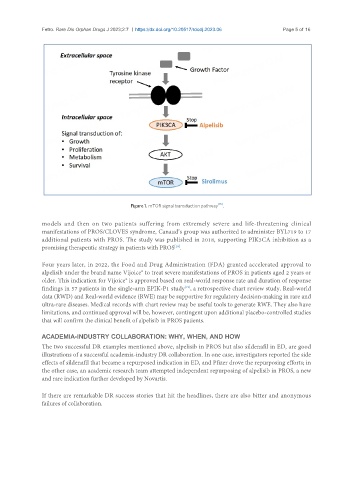
Figure 1. mTOR signal transduction pathway [15] .
models and then on two patients suffering from extremely severe and life-threatening clinical
manifestations of PROS/CLOVES syndrome, Canaud’s group was authorized to administer BYL719 to 17
additional patients with PROS. The study was published in 2018, supporting PIK3CA inhibition as a
promising therapeutic strategy in patients with PROS .
[18]
Four years later, in 2022, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted accelerated approval to
alpelisib under the brand name Vijoice® to treat severe manifestations of PROS in patients aged 2 years or
older. This indication for Vijoice® is approved based on real-world response rate and duration of response
[19]
findings in 57 patients in the single-arm EPIK-P1 study , a retrospective chart review study. Real-world
data (RWD) and Real-world evidence (RWE) may be supportive for regulatory decision-making in rare and
ultra-rare diseases. Medical records with chart review may be useful tools to generate RWE. They also have
limitations, and continued approval will be, however, contingent upon additional placebo-controlled studies
that will confirm the clinical benefit of alpelisib in PROS patients.
ACADEMIA-INDUSTRY COLLABORATION: WHY, WHEN, AND HOW
The two successful DR examples mentioned above, alpelisib in PROS but also sildenafil in ED, are good
illustrations of a successful academia-industry DR collaboration. In one case, investigators reported the side
effects of sildenafil that became a repurposed indication in ED, and Pfizer drove the repurposing efforts; in
the other case, an academic research team attempted independent repurposing of alpelisib in PROS, a new
and rare indication further developed by Novartis.
If there are remarkable DR success stories that hit the headlines, there are also bitter and anonymous
failures of collaboration.