Page 321 - Read Online
P. 321
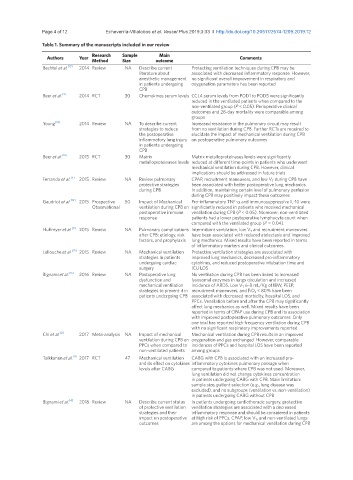
Page 4 of 12 Echeverria-Villalobos et al. Vessel Plus 2019;3:33 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2019.12
Table 1. Summary of the manuscripts included in our review
Research Sample Main
Authors Year Comments
Method Size outcome
Bechtel et al. [13] 2014 Review NA Describe current Protecting ventilation techniques during CPB may be
literature about associated with decreased inflammatory response. However,
anesthetic management no significant overall improvement in respiratory and
in patients undergoing oxygenation parameters has been reported
CPB
Beer et al. [9] 2014 RCT 30 Chemokines serum levels CCL4 serum levels from POD1 to POD5 were significantly
reduced in the ventilated patients when compared to the
non-ventilated group (P < 0.05). Perioperative clinical
outcomes and 28-day mortality were comparable among
groups
Young [14] 2014 Review NA To describe current Increased resistance in the pulmonary circuit may result
strategies to reduce from no ventilation during CPB. Further RCTs are required to
the postoperative elucidate the impact of mechanical ventilation during CPB
inflammatory lung injury on postoperative pulmonary outcomes
in patients undergoing
CPB
Beer et al. [10] 2015 RCT 30 Matrix Matrix metalloproteinases levels were significantly
metalloproteinases levels reduced at different time-points in patients who underwent
mechanical ventilation during CPB. However, clinical
implications should be addressed in future trials
Ferrando et al. [5] 2015 Review NA Review pulmonary CPAP, recruitment maneuvers, and low V T during CPB have
protective strategies been associated with better postoperative lung mechanics.
during CPB In addition, maintaining certain level of pulmonary perfusion
during CPB may positively impact these outcomes
Gaudriot et al. [12] 2015 Prospective 50 Impact of Mechanical Pro-inflammatory TNF-α and immunosuppressive IL-10 were
Observational ventilation during CPB on significantly reduced in patients who received mechanical
postoperative immune ventilation during CPB (P < 0.05). Moreover, non-ventilated
response patients had a lower postoperative lymphocyte count when
compared with the ventilated group (P = 0.04).
Huffmyer et al. [6] 2015 Review NA Pulmonary complications Intermittent ventilation, low V T and recruitment maneuvers
after CPB: etiology, risk have been associated with reduced atelectasis and improved
factors, and prophylaxis lung mechanics. Mixed results have been reported in terms
of inflammatory markers and clinical outcomes.
Lellouche et al. [15] 2015 Review NA Mechanical ventilation Protective ventilation strategies are associated with
strategies In patients improved lung mechanics, decreased pro-inflammatory
undergoing cardiac cytokines, and reduced postoperative intubation time and
surgery ICU LOS
Bignami et al. [16] 2016 Review NA Postoperative lung No ventilation during CPB has been linked to increased
dysfunction and lysosomal enzymes in lungs circulation and increased
mechanical ventilation incidence of ARDS. Low V T 6-8 mL/Kg of IBW, PEEP,
strategies to prevent it in recruitment maneuvers, and FiO 2 < 80% have been
patients undergoing CPB associated with decreased morbidity, hospital LOS, and
PPCs. Ventilation before and after the CPB may significantly
affect lung mechanics as well. Mixed results have been
reported in terms of CPAP use during CPB and its association
with improved postoperative pulmonary outcomes. Only
one trial has reported high-frequency ventilation during CPB
with no significant respiratory improvements reported
Chi et al. [8] 2017 Meta-analysis NA Impact of mechanical Mechanical ventilation during CPB results in an improved
ventilation during CPB on oxygenation and gas exchanged. However, comparable
PPCs when compared to incidences of PPCs and hospital LOS have been reported
non-ventilated patients among groups
Toikkanen et al. [11] 2017 RCT 47 Mechanical ventilation CABG with CPB is associated with an increased pro-
and its effect on cytokines inflammatory cytokines pulmonary passage when
levels after CABG compared to patients where CPB was not used. Moreover,
lung ventilation did not change cytokines concentration
in patients undergoing CABG with CPB. Main limitation:
sample size, patient selection (e.g., lung disease was
excluded), and no subgroups (ventilation vs. non-ventilation)
in patients undergoing CABG without CPB
Bignami et al. [4] 2018 Review NA Describe current status In patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery, protective
of protective ventilation ventilation strategies are associated with a decreased
strategies and their inflammatory response and should be considered in patients
impact on postoperative at high risk of PPCs. CPAP, low V T , and non-ventilated lungs
outcomes are among the options for mechanical ventilation during CPB