Page 254 - Read Online
P. 254
Page 6 of 9 Lam et al. Vessel Plus 2019;3:27 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2019.009
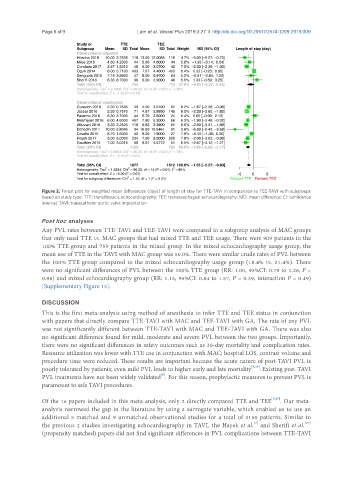
Figure 2. Forest plot for weighted mean differences (days) of length of stay for TTE-TAVI in comparison to TEE-TAVI with subgroups
based on study type. TTE: transthoracic echocardiography; TEE: transesophageal echocardiography; MD: mean difference; CI: confidence
interval; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation
Post hoc analyses
Any PVL rates between TTE-TAVI and TEE-TAVI were compared in a subgroup analysis of MAC groups
that only used TTE vs. MAC groups that had mixed TTE and TEE usage. There were 909 patients in the
100% TTE group and 755 patients in the mixed group. In the mixed echocardiography usage group, the
mean use of TTE in the TAVI with MAC group was 50.0%. There were similar crude rates of PVL between
the 100% TTE group compared to the mixed echocardiography usage group (18.4% vs. 21.4%). There
were no significant differences of PVL between the 100% TTE group (RR: 1.00, 95%CI: 0.79 to 1.26, P =
0.98) and mixed echocardiography group (RR: 1.15, 95%CI: 0.84 to 1.57, P = 0.39, interaction P = 0.49)
[Supplementary Figure 13].
DISCUSSION
This is the first meta-analysis using method of anesthesia to infer TTE and TEE status in conjunction
with papers that directly compare TTE-TAVI with MAC and TEE-TAVI with GA. The rate of any PVL
was not significantly different between TTE-TAVI with MAC and TEE-TAVI with GA. There was also
no significant difference found for mild, moderate and severe PVL between the two groups. Importantly,
there were no significant differences in safety outcomes such as 30-day mortality and complication rates.
Resource utilization was lower with TTE use in conjunction with MAC; hospital LOS, contrast volume and
procedure time were reduced. These results are important because the acute nature of post-TAVI PVL is
poorly tolerated by patients; even mild PVL leads to higher early and late mortality [9,28] .Existing post-TAVI
[9]
PVL treatments have not been widely validated . For this reason, prophylactic measures to prevent PVL is
paramount to safe TAVI procedures.
Of the 16 papers included in this meta-analysis, only 2 directly compared TTE and TEE [7,27] . Our meta-
analysis narrowed the gap in the literature by using a surrogate variable, which enabled us to use an
additional 5 matched and 9 unmatched observational studies for a total of 3150 patients. Similar to
[7]
[27]
the previous 2 studies investigating echocardiography in TAVI, the Hayek et al. and Sherifi et al.
(propensity matched) papers did not find significant differences in PVL complications between TTE-TAVI