Page 362 - Read Online
P. 362
Page 4 of 9 Nedogoda et al. Vessel Plus 2018;2:37 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2018.36
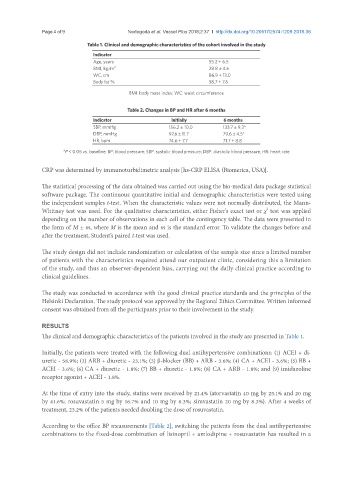
Table 1. Clinical and demographic characteristics of the cohort involved in the study
Indicator
Age, years 55.2 ± 6.5
BMI, kg/m 2 28.8 ± 4.6
WC, cm 86.9 ± 13.0
Body fat % 38.7 ± 7.6
BMI: body mass index; WC: waist circumference
Table 2. Changes in BP and HR after 6 months
Indicator Initially 6 months
SBP, mmHg 156.2 ± 10.0 133.7 ± 9.3*
DBP, mmHg 97.6 ± 11.7 79.6 ± 4.5*
HR, bpm 74.6 ± 7.7 71.7 ± 8.8
*P < 0.05 vs. baseline; BP: blood pressure; SBP: systolic blood pressure; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; HR: heart rate
CRP was determined by immunoturbidimetric analysis [hs-CRP ELISA (Biomerica, USA)].
The statistical processing of the data obtained was carried out using the bio-medical data package statistical
software package. The continuous quantitative initial and demographic characteristics were tested using
the independent samples t-test. When the characteristic values were not normally distributed, the Mann-
2
Whitney test was used. For the qualitative characteristics, either Fisher’s exact test or χ test was applied
depending on the number of observations in each cell of the contingency table. The data were presented in
the form of M ± m, where М is the mean and m is the standard error. To validate the changes before and
after the treatment, Student’s paired t-test was used.
The study design did not include randomization or calculation of the sample size since a limited number
of patients with the characteristics required attend our outpatient clinic, considering this a limitation
of the study, and thus an observer-dependent bias, carrying out the daily clinical practice according to
clinical guidelines.
The study was conducted in accordance with the good clinical practice standards and the principles of the
Helsinki Declaration. The study protocol was approved by the Regional Ethics Committee. Written informed
consent was obtained from all the participants prior to their involvement in the study.
RESULTS
The clinical and demographic characteristics of the patients involved in the study are presented in Table 1.
Initially, the patients were treated with the following dual antihypertensive combinations: (1) ACEI + di-
uretic - 58.9%; (2) ARB + diuretic - 23.1%; (3) β-blocker (BB) + ARB - 3.6%; (4) CA + ACEI - 3.6%; (5) BB +
ACEI - 3.6%; (6) CA + diuretic - 1.8%; (7) BB + diuretic - 1.8%; (8) CA + ARB - 1.8%; and (9) imidazoline
receptor agonist + ACEI - 1.8%.
At the time of entry into the study, statins were received by 21.4% (atorvastatin 40 mg by 25.1% and 20 mg
by 41.6%; rosuvastatin 5 mg by 16.7% and 10 mg by 8.3%; simvastatin 20 mg by 8.3%). After 4 weeks of
treatment, 23.2% of the patients needed doubling the dose of rosuvastatin.
According to the office BP measurements [Table 2], switching the patients from the dual antihypertensive
combinations to the fixed-dose combination of lisinopril + amlodipine + rosuvastatin has resulted in a