Page 363 - Read Online
P. 363
Nedogoda et al. Vessel Plus 2018;2:37 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2018.36 Page 5 of 9
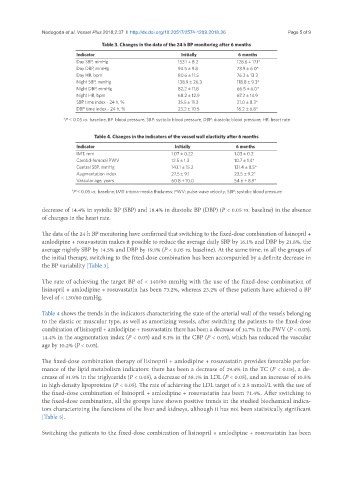
Table 3. Changes in the data of the 24 h BP monitoring after 6 months
Indicator Initially 6 months
Day SBP, mmHg 153.1 ± 8.2 128.6 ± 17.1*
Day DBP, mmHg 94.5 ± 9.8 73.9 ± 6.0*
Day HR, bpm 80.6 ± 11.5 76.3 ± 13.2
Night SBP, mmHg 138.9 ± 26.3 118.8 ± 9.3*
Night DBP, mmHg 82,2 ± 11,8 66.5 ± 6.0*
Night HR, bpm 68.2 ± 12.9 67.2 ± 14.9
SBP time index - 24 h, % 35.5 ± 11.3 21.0 ± 8.3*
DBP time index - 24 h, % 23.2 ± 10.5 16.2 ± 6.8*
*P < 0.05 vs. baseline; BP: blood pressure; SBP: systolic blood pressure; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; HR: heart rate
Table 4. Changes in the indicators of the vessel wall elasticity after 6 months
Indicator Initially 6 months
IMT, mm 1.07 ± 0.22 1.03 ± 0.2
Carotid-femoral PWV 12.5 ± 1.3 10.7 ± 1.4*
Central SBP, mmHg 143.1 ± 15.2 131.4 ± 8.5*
Augmentation index 27.5 ± 9.1 23.5 ± 9.2*
Vascular age, years 60.8 ± 10.0 54.6 ± 8.9*
*P < 0.05 vs. baseline; IMT: intima-media thickness; PWV: pulse wave velocity; SBP: systolic blood pressure
decrease of 14.4% in systolic BP (SBP) and 18.4% in diastolic BP (DBP) (P < 0.05 vs. baseline) in the absence
of changes in the heart rate.
The data of the 24 h BP monitoring have confirmed that switching to the fixed-dose combination of lisinopril +
amlodipine + rosuvastatin makes it possible to reduce the average daily SBP by 16.1% and DBP by 21.8%, the
average nightly SBP by 14.5% and DBP by 19.1% (P < 0.05 vs. baseline). At the same time, in all the groups of
the initial therapy, switching to the fixed-dose combination has been accompanied by a definite decrease in
the BP variability [Table 3].
The rate of achieving the target BP of < 140/90 mmHg with the use of the fixed-dose combination of
lisinopril + amlodipine + rosuvastatin has been 73.2%, whereas 23.2% of these patients have achieved a BP
level of < 130/80 mmHg.
Table 4 shows the trends in the indicators characterizing the state of the arterial wall of the vessels belonging
to the elastic or muscular type, as well as amortizing vessels, after switching the patients to the fixed-dose
combination of lisinopril + amlodipine + rosuvastatin: there has been a decrease of 14.7% in the PWV (P < 0.05),
14.4% in the augmentation index (P < 0.05) and 8.1% in the CBP (P < 0.05), which has reduced the vascular
age by 10.2% (P < 0.05).
The fixed-dose combination therapy of lisinopril + amlodipine + rosuvastatin provides favorable perfor-
mance of the lipid metabolism indicators: there has been a decrease of 29.4% in the TC (P < 0.05), a de-
crease of 31.9% in the triglycerids (P < 0.05), a decrease of 38.1% in LDL (P < 0.05), and an increase of 10.5%
in high-density lipoproteins (P < 0.05). The rate of achieving the LDL target of ≤ 2.5 mmol/L with the use of
the fixed-dose combination of lisinopril + amlodipine + rosuvastatin has been 71.4%. After switching to
the fixed-dose combination, all the groups have shown positive trends in the studied biochemical indica-
tors characterizing the functions of the liver and kidneys, although it has not been statistically significant
[Table 5].
Switching the patients to the fixed-dose combination of lisinopril + amlodipine + rosuvastatin has been