Page 23 - Read Online
P. 23
Page 12 of 24 Rao. Vessel Plus 2022;6:22 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.105
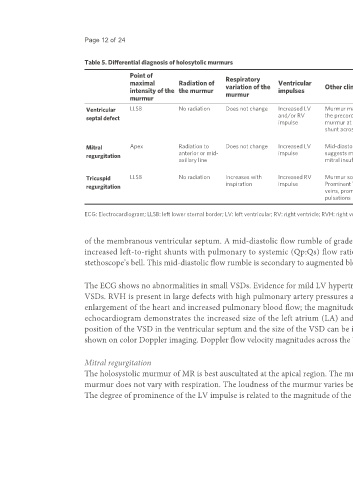
Table 5. Differential diagnosis of holosytolic murmurs
Point of Respiratory
maximal Radiation of variation of the Ventricular Other clinical findings Chest X-ray ECG Echo Doppler
intensity of the the murmur murmur impulses
murmur
Ventricular LLSB No radiation Does not change Increased LV Murmur may be widely heard over Cardiomegaly, increased LVH, VSD can be imaged by 2D echo.
septal defect and/or RV the precordium. Mid-diastolic pulmonary vascular biventricular Doppler flow velocity across the
impulse murmur at apex suggests a large markings hypertrophy VSD is helpful in assessing the
shunt across the VSD (BVH) size of VSD
or RVH
Mitral Apex Radiation to Does not change Increased LV Mid-diastolic murmur at apex Cardiomegaly, left atrial LAE, LVH Color Doppler evidence for
anterior or mid- impulse suggests moderate to severe enlargement (LAE), normal mitral insufficiency
regurgitation
axillary line mitral insufficiency pulmonary vascular
markings
Tricuspid LLSB No radiation Increases with Increased RV Murmur sounds “superficial”. Cardiomegaly, large right RVH, right atrial Color Doppler evidence for
regurgitation inspiration impulse Prominent V-waves in jugular atrium enlargement tricuspid insufficiency
veins, prominent systolic hepatic (RAE)
pulsations
ECG: Electrocardiogram; LLSB: left lower sternal border; LV: left ventricular; RV: right ventricle; RVH: right ventricular hypertrophy; VSD: ventricular septal defect.
of the membranous ventricular septum. A mid-diastolic flow rumble of grade I to II/VI intensity is auscultated slightly internal to the apex in subjects with
increased left-to-right shunts with pulmonary to systemic (Qp:Qs) flow ratio ≥ 2:1 (medium and large VSDs). This murmur is auscultated best with the
stethoscope’s bell. This mid-diastolic flow rumble is secondary to augmented blood flow via the mitral valve. The BP and peripheral pulses are usually normal.
The ECG shows no abnormalities in small VSDs. Evidence for mild LV hypertrophy is seen in moderate-sized VSDs. Biventricular hypertrophy has seen large
VSDs. RVH is present in large defects with high pulmonary artery pressures and those who have developed PVOD. Chest roentgenogram usually shows an
enlargement of the heart and increased pulmonary blood flow; the magnitude of such abnormalities is proportionate to the diameter of the VSD. M-mode
echocardiogram demonstrates the increased size of the left atrium (LA) and LV; these changes are again are proportional to the size of the VSD . The
[20]
position of the VSD in the ventricular septum and the size of the VSD can be imaged by 2D echocardiography. Left-to-right shunting across the VSD can be
shown on color Doppler imaging. Doppler flow velocity magnitudes across the VSD are useful in estimating the size of the VSD and the PA pressure.
Mitral regurgitation
The holosystolic murmur of MR is best auscultated at the apical region. The murmur transmits well into the anterior or mid-axillary sites. The loudness of the
murmur does not vary with respiration. The loudness of the murmur varies between grades II and IV/VI. The LV impulse is prominent and hyper-dynamic.
The degree of prominence of the LV impulse is related to the magnitude of the MR. A systolic thrill may be felt at the apical region. The 2nd sound is split in a