Page 42 - Read Online
P. 42
Page 6 of 9 Xu et al. Vessel Plus 2023;7:33 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2023.98
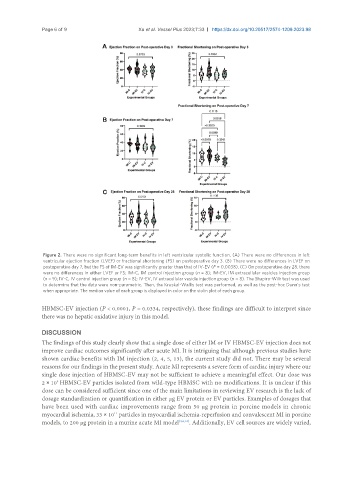
Figure 2. There were no significant long-term benefits in left ventricular systolic function. (A) There were no differences in left
ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) or fractional shortening (FS) on postoperative day 3. (B) There were no differences in LVEF on
postoperative day 7, but the FS of IM-EV was significantly greater than that of IV-EV (P = 0.0038). (C) On postoperative day 28, there
were no differences in either LVEF or FS; IM-C, IM control injection group (n = 8); IM-EV, IM extracellular vesicles injection group
(n = 9); IV-C, IV control injection group (n = 8); IV-EV, IV extracellular vesicle injection group (n = 8). The Shapiro-Wilk test was used
to determine that the data were non-parametric. Then, the Kruskal-Wallis test was performed, as well as the post-hoc Dunn’s test
when appropriate. The median value of each group is displayed in color on the violin plot of each group.
HBMSC-EV injection (P < 0.0001, P = 0.0334, respectively), these findings are difficult to interpret since
there was no hepatic oxidative injury in this model.
DISCUSSION
The findings of this study clearly show that a single dose of either IM or IV HBMSC-EV injection does not
improve cardiac outcomes significantly after acute MI. It is intriguing that although previous studies have
shown cardiac benefits with IM injection (2, 4, 5, 13), the current study did not. There may be several
reasons for our findings in the present study. Acute MI represents a severe form of cardiac injury where our
single dose injection of HBMSC-EV may not be sufficient to achieve a meaningful effect. Our dose was
2 × 10 HBMSC-EV particles isolated from wild-type HBMSC with no modifications. It is unclear if this
9
dose can be considered sufficient since one of the main limitations in reviewing EV research is the lack of
dosage standardization or quantification in either µg EV protein or EV particles. Examples of dosages that
have been used with cardiac improvements range from 50 µg protein in porcine models in chronic
myocardial ischemia, 33 × 10 particles in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion and convalescent MI in porcine
11
models, to 200 µg protein in a murine acute MI model [4,6,13] . Additionally, EV cell sources are widely varied,