Page 244 - Read Online
P. 244
Sufali et al. Vessel Plus 2024;8:16 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2023.139 Page 9 of 14
Table 5. Main characteristics of the patients who presented SCI
Crawford ‘s MEPs SCI-grade SCI-grade Cerebral 30-day/in-H
Case CSFD Staging SCI-timing * *
extent SSEPs @Onset @Discharge hemorrhage mortality
1 III Yes No No 1st POD 0 0 No No
2 III Yes No Yes @Awakening, 3 4 No No
After I Step
3 II Yes No Yes @Awakening, 3 - No Yes
After I Step
4 III Yes No No @Awakening 2 2 No No
5 II Yes No Yes @Awakening, 4 4 Yes No
After II Step
6 II Yes Yes Yes @Awakening, 0 - Yes Yes
After I Step
7 III Yes Yes No > 24 h 4 5 No No
8 III Yes No No > 24 h 4 5 No No
POD: Post-operative day. *According with the Tarlov’s Modified Scale.
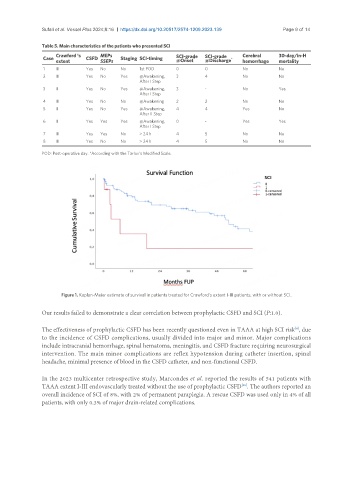
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier estimate of survival in patients treated for Crawford’s extent I-III patients, with or without SCI.
Our results failed to demonstrate a clear correlation between prophylactic CSFD and SCI (P:1.0).
The effectiveness of prophylactic CSFD has been recently questioned even in TAAA at high SCI risk , due
[4]
to the incidence of CSFD complications, usually divided into major and minor. Major complications
include intracranial hemorrhage, spinal hematoma, meningitis, and CSFD fracture requiring neurosurgical
intervention. The main minor complications are reflex hypotension during catheter insertion, spinal
headache, minimal presence of blood in the CSFD catheter, and non-functional CSFD.
In the 2023 multicenter retrospective study, Marcondes et al. reported the results of 541 patients with
[25]
TAAA extent I-III endovascularly treated without the use of prophylactic CSFD . The authors reported an
overall incidence of SCI of 8%, with 2% of permanent paraplegia. A rescue CSFD was used only in 4% of all
patients, with only 0.3% of major drain-related complications.