Page 34 - Read Online
P. 34
Bros-Facer et al. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2023;2:21 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2023.26 Page 7 of 14
Figure 3. Timing for providing information, securing informed consent and enrollment.
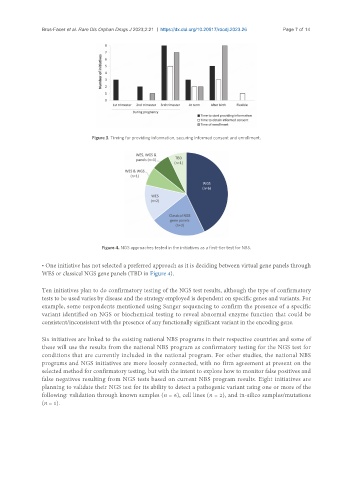
Figure 4. NGS approaches tested in the initiatives as a first-tier test for NBS.
• One initiative has not selected a preferred approach as it is deciding between virtual gene panels through
WES or classical NGS gene panels (TBD in Figure 4).
Ten initiatives plan to do confirmatory testing of the NGS test results, although the type of confirmatory
tests to be used varies by disease and the strategy employed is dependent on specific genes and variants. For
example, some respondents mentioned using Sanger sequencing to confirm the presence of a specific
variant identified on NGS or biochemical testing to reveal abnormal enzyme function that could be
consistent/inconsistent with the presence of any functionally significant variant in the encoding gene.
Six initiatives are linked to the existing national NBS programs in their respective countries and some of
these will use the results from the national NBS program as confirmatory testing for the NGS test for
conditions that are currently included in the national program. For other studies, the national NBS
programs and NGS initiatives are more loosely connected, with no firm agreement at present on the
selected method for confirmatory testing, but with the intent to explore how to monitor false positives and
false negatives resulting from NGS tests based on current NBS program results. Eight initiatives are
planning to validate their NGS test for its ability to detect a pathogenic variant using one or more of the
following: validation through known samples (n = 6), cell lines (n = 2), and in-silico samples/mutations
(n = 1).