Page 841 - Read Online
P. 841
Favre et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:71 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2020.149 Page 3 of 12
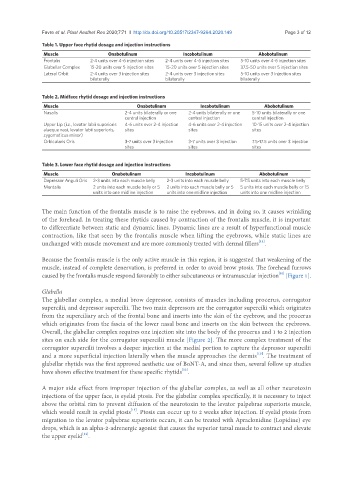
Table 1. Upper face rhytid dosage and injection instructions
Muscle Onabotulinum Incobotulinum Abobotulinum
Frontalis 2-4 units over 4-6 injection sites 2-4 units over 4-6 injection sites 5-10 units over 4-6 injection sites
Glabellar Complex 15-20 units over 5 injection sites 15-20 units over 5 injection sites 37.5-50 units over 5 injection sites
Lateral Orbit 2-4 units over 3 injection sites 2-4 units over 3 injection sites 5-10 units over 3 injection sites
bilaterally bilaterally bilaterally
Table 2. Midface rhytid dosage and injection instructions
Muscle Onabotulinum Incobotulinum Abobotulinum
Nasalis 2-4 units bilaterally or one 2-4 units bilaterally or one 5-10 units bilaterally or one
central injection central injection central injection
Upper Lip (i.e., levator labii superioris 4-6 units over 2-4 injection 4-6 units over 2-4 injection 10-15 units over 2-4 injection
alaeque nasi, levator labii superioris, sites sites sites
zygomaticus minor)
Orbicularis Oris 3-7 units over 3 injection 3-7 units over 3 injection 7.5-17.5 units over 3 injection
sites sites sites
Table 3. Lower face rhytid dosage and injection instructions
Muscle Onabotulinum Incobotulinum Abobotulinum
Depressor Anguli Oris 2-3 units into each muscle belly 2-3 units into each muscle belly 5-7.5 units into each muscle belly
Mentalis 2 units into each muscle belly or 5 2 units into each muscle belly or 5 5 units into each muscle belly or 15
units into one midline injection units into one midline injection units into one midline injection
The main function of the frontalis muscle is to raise the eyebrows, and in doing so, it causes wrinkling
of the forehead. In treating these rhytids caused by contraction of the frontalis muscle, it is important
to differentiate between static and dynamic lines. Dynamic lines are a result of hyperfunctional muscle
contraction, like that seen by the frontalis muscle when lifting the eyebrows, while static lines are
[11]
unchanged with muscle movement and are more commonly treated with dermal fillers .
Because the frontalis muscle is the only active muscle in this region, it is suggested that weakening of the
muscle, instead of complete denervation, is preferred in order to avoid brow ptosis. The forehead furrows
caused by the frontalis muscle respond favorably to either subcutaneous or intramuscular injection [Figure 1].
[10]
Glabella
The glabellar complex, a medial brow depressor, consists of muscles including procerus, corrugator
supercilii, and depressor supercilii. The two main depressors are the corrugator supercilii which originates
from the superciliary arch of the frontal bone and inserts into the skin of the eyebrow, and the procerus
which originates from the fascia of the lower nasal bone and inserts on the skin between the eyebrows.
Overall, the glabellar complex requires one injection site into the body of the procerus and 1 to 2 injection
sites on each side for the corrugator supercilii muscle [Figure 2]. The more complex treatment of the
corrugator supercilii involves a deeper injection at the medial portion to capture the depressor supercilii
and a more superficial injection laterally when the muscle approaches the dermis . The treatment of
[10]
glabellar rhytids was the first approved aesthetic use of BoNT-A, and since then, several follow up studies
have shown effective treatment for these specific rhytids .
[12]
A major side effect from improper injection of the glabellar complex, as well as all other neurotoxin
injections of the upper face, is eyelid ptosis. For the glabellar complex specifically, it is necessary to inject
above the orbital rim to prevent diffusion of the neurotoxin to the levator palpebrae superioris muscle,
[13]
which would result in eyelid ptosis . Ptosis can occur up to 2 weeks after injection. If eyelid ptosis from
migration to the levator palpebrae superioris occurs, it can be treated with Apraclonidine (Lopidine) eye
drops, which is an alpha-2-adrenergic agonist that causes the superior tarsal muscle to contract and elevate
[14]
the upper eyelid .