Page 125 - Read Online
P. 125
Campbell et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:12 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2019.59 Page 5 of 6
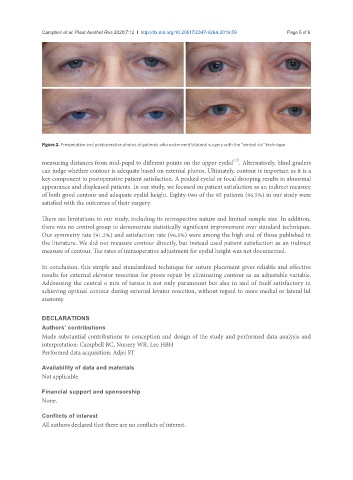
Figure 2. Preoperative and postoperative photos of patients who underwent bilateral surgery with the “central six” technique
[12]
measuring distances from mid-pupil to different points on the upper eyelid . Alternatively, blind graders
can judge whether contour is adequate based on external photos. Ultimately, contour is important as it is a
key component to postoperative patient satisfaction. A peaked eyelid or focal drooping results in abnormal
appearance and displeased patients. In our study, we focused on patient satisfaction as an indirect measure
of both good contour and adequate eyelid height. Eighty-two of the 85 patients (96.5%) in our study were
satisfied with the outcomes of their surgery.
There are limitations to our study, including its retrospective nature and limited sample size. In addition,
there was no control group to demonstrate statistically significant improvement over standard techniques.
Our symmetry rate (91.2%) and satisfaction rate (96.5%) were among the high end of those published in
the literature. We did not measure contour directly, but instead used patient satisfaction as an indirect
measure of contour. The rates of intraoperative adjustment for eyelid height was not documented.
In conclusion, this simple and standardized technique for suture placement gives reliable and effective
results for external elevator resection for ptosis repair by eliminating contour as an adjustable variable.
Addressing the central 6 mm of tarsus is not only paramount but also in and of itself satisfactory in
achieving optimal contour during external levator resection, without regard to more medial or lateral lid
anatomy.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Made substantial contributions to conception and design of the study and performed data analysis and
interpretation: Campbell BC, Nunery WR, Lee HBH
Performed data acquisition: Adjei ST
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Financial support and sponsorship
None.
Conflicts of interest
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.