Page 107 - Read Online
P. 107
Wiedner et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:10 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2019.51 Page 3 of 10
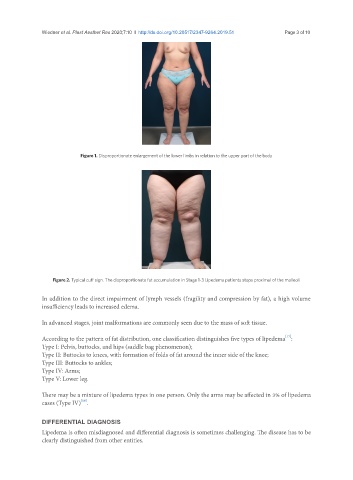
Figure 1. Disproportionate enlargement of the lower limbs in relation to the upper part of the body
Figure 2. Typical cuff sign. The disproportionate fat accumulation in Stage 1-3 Lipedema patients stops proximal of the malleoli
In addition to the direct impairment of lymph vessels (fragility and compression by fat), a high volume
insufficiency leads to increased edema.
In advanced stages, joint malformations are commonly seen due to the mass of soft tissue.
[17]
According to the pattern of fat distribution, one classification distinguishes five types of lipedema :
Type I: Pelvis, buttocks, and hips (saddle bag phenomenon);
Type II: Buttocks to knees, with formation of folds of fat around the inner side of the knee;
Type III: Buttocks to ankles;
Type IV: Arms;
Type V: Lower leg.
There may be a mixture of lipedema types in one person. Only the arms may be affected in 3% of lipedema
[18]
cases (Type IV) .
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Lipedema is often misdiagnosed and differential diagnosis is sometimes challenging. The disease has to be
clearly distinguished from other entities.