Page 320 - Read Online
P. 320
Page 6 of 9 Lee et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:43 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2018.39
Table 2. Summary of hyaluronic acid dermal fillers currently commercially available in the United States. All except for
Belotero Balance contain lidocaine
Product ® Site HA concentration (mg/mL) Duration (approximate months)
Belotero Balance Superficial - mid-dermis 22.5 6
Restylane-L Superficial - mid-dermis 20 6
Restylane Silk Superficial - sub-mucosal 20 6
Restylane Lyft Medium - deep 20 9
Restylane Refyne Medium - deep 20 12
Restylane Defyne Medium - deep 20 12
Juvederm Ultra XC Superficial - medium 24 12
Juvederm Volbella Superficial - medium 15 12-18
Juvederm Vollure Medium - deep 17.5 12-18
Juvederm Voluma XC Medium - deep 20 12-18
Juvederm Ultra Plus XC Medium - deep 24 18
HA: hyaluronic acid
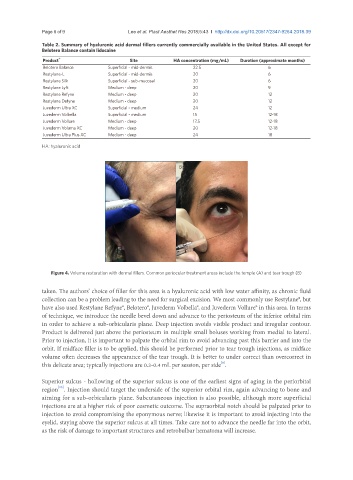
A B
Figure 4. Volume restoration with dermal fillers. Common periocular treatment areas include the temple (A) and tear trough (B)
taken. The authors’ choice of filler for this area is a hyaluronic acid with low water affinity, as chronic fluid
collection can be a problem leading to the need for surgical excision. We most commonly use Restylane®, but
have also used Restylane Refyne®, Belotero®, Juvederm Volbella®, and Juvederm Vollure® in this area. In terms
of technique, we introduce the needle bevel down and advance to the periosteum of the inferior orbital rim
in order to achieve a sub-orbicularis plane. Deep injection avoids visible product and irregular contour.
Product is delivered just above the periosteum in multiple small boluses working from medial to lateral.
Prior to injection, it is important to palpate the orbital rim to avoid advancing past this barrier and into the
orbit. If midface filler is to be applied, this should be performed prior to tear trough injections, as midface
volume often decreases the appearance of the tear trough. It is better to under correct than overcorrect in
[8]
this delicate area; typically injections are 0.3-0.4 mL per session, per side .
Superior sulcus - hollowing of the superior sulcus is one of the earliest signs of aging in the periorbital
[13]
region . Injection should target the underside of the superior orbital rim, again advancing to bone and
aiming for a sub-orbicularis plane. Subcutaneous injection is also possible, although more superficial
injections are at a higher risk of poor cosmetic outcome. The supraorbital notch should be palpated prior to
injection to avoid compromising the eponymous nerve; likewise it is important to avoid injecting into the
eyelid, staying above the superior sulcus at all times. Take care not to advance the needle far into the orbit,
as the risk of damage to important structures and retrobulbar hematoma will increase.