Page 317 - Read Online
P. 317
Lee et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:43 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2018.39 Page 3 of 9
Table 1. Properties of commercially available botulinum toxin products
®
Botox onabotulinumtoxinA Dysport abobotulinumtoxinA Xeomin incobotulinumtoxinA
®
®
Molecular weight 900 kD ≥ 300 kD 150 kD
Preparation Vacuum dried NaCl + albumin Lyophilized lactose + albumin Lyophilized albumin + sucrose
pH Neutral Neutral Neutral
Vial size 50 and 100 units 300 units 50 and 100 units
Storage temperature 2-8 ℃ 2-8 ℃ Room Temperature
Other Contraindicated if cow milk Retention of particles under lid requires tilting
protein allergy after reconstitution to capture all product
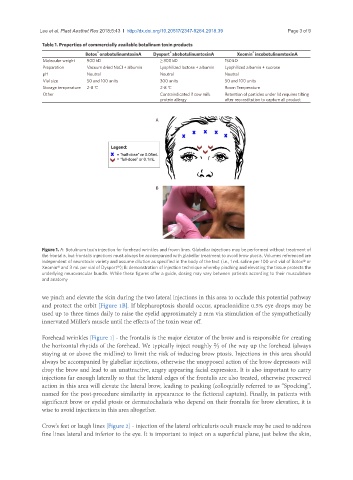
A
B
Figure 1. A: Botulinum toxin injection for forehead wrinkles and frown lines. Glabellar injections may be performed without treatment of
the frontalis, but frontalis injections must always be accompanied with glabellar treatment to avoid brow ptosis. Volumes referenced are
independent of neurotoxin variety and assume dilution as specified in the body of the text (i.e., 1 mL saline per 100 unit vial of Botox® or
Xeomin® and 3 mL per vial of Dysport®); B: demonstration of injection technique whereby pinching and elevating the tissue protects the
underlying neurovascular bundle. While these figures offer a guide, dosing may vary between patients according to their musculature
and anatomy
we pinch and elevate the skin during the two lateral injections in this area to occlude this potential pathway
and protect the orbit [Figure 1B]. If blepharoptosis should occur, apraclonidine 0.5% eye drops may be
used up to three times daily to raise the eyelid approximately 2 mm via stimulation of the sympathetically
innervated Müller’s muscle until the effects of the toxin wear off.
Forehead wrinkles [Figure 1] - the frontalis is the major elevator of the brow and is responsible for creating
the horizontal rhytids of the forehead. We typically inject roughly ⅔ of the way up the forehead (always
staying at or above the midline) to limit the risk of inducing brow ptosis. Injections in this area should
always be accompanied by glabellar injections, otherwise the unopposed action of the brow depressors will
drop the brow and lead to an unattractive, angry appearing facial expression. It is also important to carry
injections far enough laterally so that the lateral edges of the frontalis are also treated, otherwise preserved
action in this area will elevate the lateral brow, leading to peaking (colloquially referred to as “Spocking”,
named for the post-procedure similarity in appearance to the fictional captain). Finally, in patients with
significant brow or eyelid ptosis or dermatochalasis who depend on their frontalis for brow elevation, it is
wise to avoid injections in this area altogether.
Crow’s feet or laugh lines [Figure 2] - injection of the lateral orbicularis oculi muscle may be used to address
fine lines lateral and inferior to the eye. It is important to inject on a superficial plane, just below the skin,