Page 162 - Read Online
P. 162
Page 4 of 9 Dutta et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:20 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2018.19
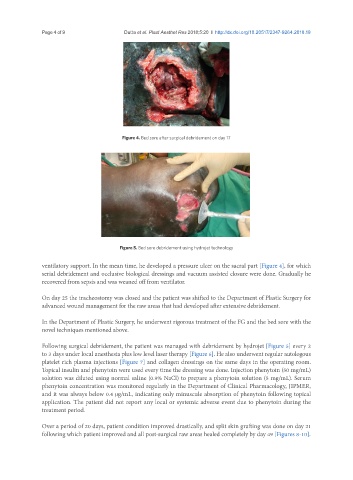
Figure 4. Bed sore after surgical debridement on day 17
Figure 5. Bed sore debridement using hydrojet technology
ventilatory support. In the mean time, he developed a pressure ulcer on the sacral part [Figure 4], for which
serial debridement and occlusive biological dressings and vacuum assisted closure were done. Gradually he
recovered from sepsis and was weaned off from ventilator.
On day 25 the tracheostomy was closed and the patient was shifted to the Department of Plastic Surgery for
advanced wound management for the raw areas that had developed after extensive debridement.
In the Department of Plastic Surgery, he underwent rigorous treatment of the FG and the bed sore with the
novel techniques mentioned above.
Following surgical debridement, the patient was managed with debridement by hydrojet [Figure 5] every 2
to 3 days under local anesthesia plus low level laser therapy [Figure 6]. He also underwent regular autologous
platelet rich plasma injections [Figure 7] and collagen dressings on the same days in the operating room.
Topical insulin and phenytoin were used every time the dressing was done. Injection phenytoin (50 mg/mL)
solution was diluted using normal saline (0.9% NaCl) to prepare a phenytoin solution (5 mg/mL). Serum
phenytoin concentration was monitored regularly in the Department of Clinical Pharmacology, JIPMER,
and it was always below 0.4 μg/mL, indicating only minuscule absorption of phenytoin following topical
application. The patient did not report any local or systemic adverse event due to phenytoin during the
treatment period.
Over a period of 20 days, patient condition improved drastically, and split skin grafting was done on day 21
following which patient improved and all post-surgical raw areas healed completely by day 49 [Figures 8-10].