Page 161 - Read Online
P. 161
Dutta et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:20 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2018.19 Page 3 of 9
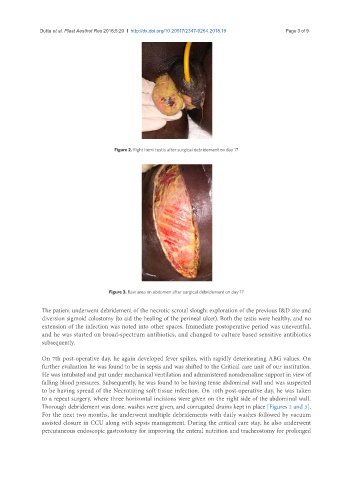
Figure 2. Right hemi testis after surgical debridement on day 17
Figure 3. Raw area on abdomen after surgical debridement on day 17
The patient underwent debridement of the necrotic scrotal slough; exploration of the previous I&D site and
diversion sigmoid colostomy (to aid the healing of the perineal ulcer). Both the testis were healthy, and no
extension of the infection was noted into other spaces. Immediate postoperative period was uneventful,
and he was started on broad-spectrum antibiotics, and changed to culture based sensitive antibiotics
subsequently.
On 7th post-operative day, he again developed fever spikes, with rapidly deteriorating ABG values. On
further evaluation he was found to be in sepsis and was shifted to the Critical care unit of our institution.
He was intubated and put under mechanical ventilation and administered noradrenaline support in view of
falling blood pressures. Subsequently, he was found to be having tense abdominal wall and was suspected
to be having spread of the Necrotizing soft tissue infection. On 10th post-operative day, he was taken
to a repeat surgery, where three horizontal incisions were given on the right side of the abdominal wall.
Thorough debridement was done, washes were given, and corrugated drains kept in place [Figures 2 and 3].
For the next two months, he underwent multiple debridements with daily washes followed by vacuum
assisted closure in CCU along with sepsis management. During the critical care stay, he also underwent
percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy for improving the enteral nutrition and tracheostomy for prolonged