Page 160 - Read Online
P. 160
Page 2 of 9 Dutta et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:20 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2018.19
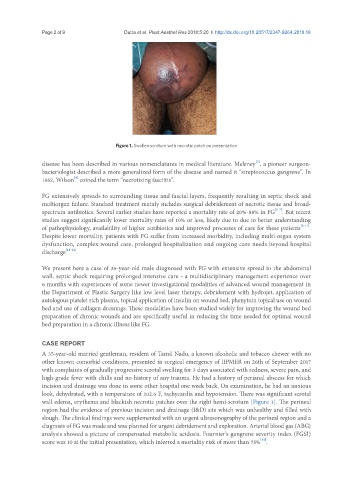
Figure 1. Swollen scrotum with necrotic patch on presentation
[3]
disease has been described in various nomenclatures in medical literature. Meleney , a pioneer surgeon-
bacteriologist described a more generalized form of the disease and named it “streptococcus gangrene”. In
[4]
1952, Wilson coined the term “necrotizing fasciitis”.
FG extensively spreads to surrounding tissue and fascial layers, frequently resulting in septic shock and
multiorgan failure. Standard treatment mainly includes surgical debridement of necrotic tissue and broad-
[5-7]
spectrum antibiotics. Several earlier studies have reported a mortality rate of 20%-88% in FG . But recent
studies suggest significantly lower mortality rates of 10% or less, likely due to due to better understanding
of pathophysiology, availability of higher antibiotics and improved processes of care for these patients [8-11] .
Despite lower mortality, patients with FG suffer from increased morbidity, including multi-organ system
dysfunction, complex wound care, prolonged hospitalization and ongoing care needs beyond hospital
discharge [12-14] .
We present here a case of 35-year-old male diagnosed with FG with extensive spread to the abdominal
wall, septic shock requiring prolonged intensive care - a multidisciplinary management experience over
6 months with experiences of some newer investigational modalities of advanced wound management in
the Department of Plastic Surgery like low level laser therapy, debridement with hydrojet, application of
autologous platelet rich plasma, topical application of insulin on wound bed, phenytoin topical use on wound
bed and use of collagen dressings. These modalities have been studied widely for improving the wound bed
preparation of chronic wounds and are specifically useful in reducing the time needed for optimal wound
bed preparation in a chronic illness like FG.
CASE REPORT
A 35-year-old married gentleman, resident of Tamil Nadu, a known alcoholic and tobacco chewer with no
other known comorbid conditions, presented in surgical emergency of JIPMER on 26th of September 2017
with complaints of gradually progressive scrotal swelling for 3 days associated with redness, severe pain, and
high-grade fever with chills and no history of any trauma. He had a history of perianal abscess for which
incision and drainage was done in some other hospital one week back. On examination, he had an anxious
look, dehydrated, with a temperature of 102.6 F, tachycardia and hypotension. There was significant scrotal
wall edema, erythema and blackish necrotic patches over the right hemi-scrotum [Figure 1]. The perineal
region had the evidence of previous incision and drainage (I&D) site which was unhealthy and filled with
slough. The clinical findings were supplemented with an urgent ultrasonography of the perineal region and a
diagnosis of FG was made and was planned for urgent debridement and exploration. Arterial blood gas (ABG)
analysis showed a picture of compensated metabolic acidosis. Fournier’s gangrene severity index (FGSI)
[15]
score was 10 at the initial presentation, which inferred a mortality risk of more than 75% .