Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
Fok et al. Skin temperature of laser for Nevus of Ota
INTRODUCTION A
Treatment lasers generate a high influx of energy over
a short period of time. As such, the energy generated
must be of high stability and precision. [1-3] Laser
techniques have been successfully and broadly used
in skin surgery. However, the various chromophores
within the skin react differently, according to the
absorption and scattering of the individual wavelengths
of the lasers used. As such, lasers of different
wavelengths can be used to treat various pathological
skin conditions.
B
A nevus fusco-caeruleus ophthalmomaxillaris
(oculodermal melanosis or Nevus of Ota) is a
syndrome consisting of blue-black or gray-brown
patchy pigmentation. It may be either unilateral or
bilateral, and most commonly occurs in the trigeminal
nerve dermatome. The lesions are present at birth
in approximately 60% of cases and occur most
commonly in patients that are of Asian descent or
dark-skinned individuals. Histologically, the melanin
[1]
pigment is seen contained within the dendritic dermal
melanocytes, similar to that in Mongolian spots. Macular
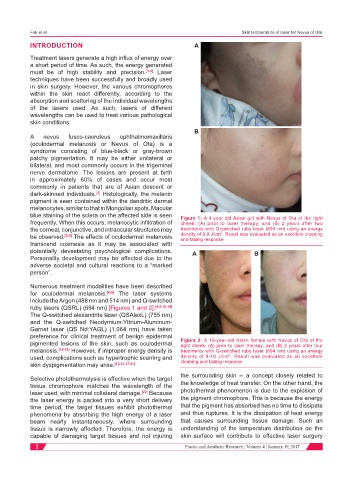
blue staining of the sclera on the affected side is seen Figure 1: A 4-year-old Asian girl with Nevus of Ota of the right
frequently. When this occurs, melanocytic infiltration of cheek: (A) prior to laser therapy; and (B) 2 years after two
the corneal, conjunctive, and intraocular structures may treatments with Q-switched ruby laser (694 nm) using an energy
2
be observed. [2-5] The effects of oculodermal melanosis density of 8-9 J/cm . Result was evaluated as an excellent cleaning
and fading response
transcend cosmesis as it may be associated with
potentially devastating psychological complications. A B
Personality development may be affected due to the
adverse societal and cultural reactions to a “marked
person”.
Numerous treatment modalities have been described
for oculodermal melanosis. [6-9] The laser systems
include the Argon (488 nm and 514 nm) and Q-switched
ruby lasers (QSRL) (694 nm) [Figures 1 and 2]. [4,5,10-14]
The Q-switched alexandrite laser (QSAlexL) (755 nm)
and the Q-switched Neodymium:Yttrium-Aluminum-
Garnet laser (QS Nd:YAGL) (1,064 nm) have taken
preference for clinical treatment of benign epidermal
pigmented lesions of the skin, such as oculodermal Figure 2: A 19-year-old Asian female with Nevus of Ota of the
right cheek: (A) prior to laser therapy; and (B) 2 years after four
melanosis. [15,16] However, if improper energy density is treatments with Q-switched ruby laser (694 nm) using an energy
2
used, complications such as hypertrophic scarring and density of 9-10 J/cm . Result was evaluated as an excellent
skin dyspigmentation may arise. [12,13,17-21] cleaning and fading response
Selective photothermolysis is effective when the target the surrounding skin -- a concept closely related to
tissue chromophore matches the wavelength of the the knowledge of heat transfer. On the other hand, the
laser used, with minimal collateral damage. [22] Because photothermal phenomenon is due to the explosion of
the laser energy is packed into a very short delivery the pigment chromophore. This is because the energy
time period, the target tissues exhibit photothermal that the pigment has absorbed has no time to dissipate
phenomena by absorbing the high energy of a laser and thus ruptures. It is the dissipation of heat energy
beam nearly instantaneously, where surrounding that causes surrounding tissue damage. Such an
tissue is narrowly affected. Therefore, the energy is understanding of the temperature distribution on the
capable of damaging target tissues and not injuring skin surface will contribute to effective laser surgery
2 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ January 19, 2017