Page 209 - Read Online
P. 209
bundle usually separates the motor from the sensory part
of the ulnar nerve. Through the forearm incision, the AIN
is identified while entering the pronator quadratus. The
dissection is carried as distal as possible into the muscle,
and the AIN is then passed dorsal to the FDP in order to
reach the motor branch of the ulnar nerve. The AIN has
[56]
at this level approximately 506 axons, whereas the ulnar
motor nerve 1523 axons. The transfer is not synergistic
[56]
and recovery is generally suboptimal, but it is sufficient to
prevent clawing of the ulnar digits.
In combined ulnar and median nerve injuries, motor
branches from the radial nerve to the extensor digiti minimi
and extensor carpi ulnaris originating from the PIN can be
used to re‑innervate the motor ulnar nerve. Coaptation is
achieved by the use of an interpositional nerve graft from
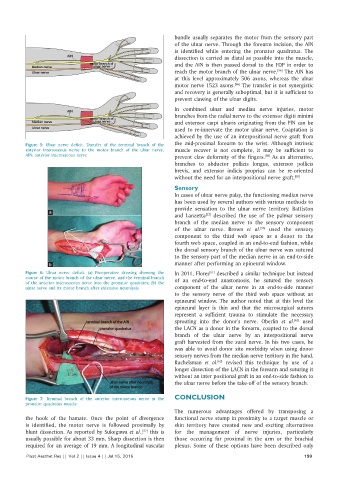
Figure 5: Ulnar nerve deficit. Transfer of the terminal branch of the the mid‑proximal forearm to the wrist. Although intrinsic
anterior interosseous nerve to the motor branch of the ulnar nerve. muscle recover is not complete, it may be sufficient to
AIN: anterior interosseous nerve prevent claw deformity of the fingers. As an alternative,
[59]
branches to abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis
brevis, and extensor indicis proprius can be re‑oriented
without the need for an interpositional nerve graft. [60]
Sensory
In cases of ulnar nerve palsy, the functioning median nerve
has been used by several authors with various methods to
provide sensation to the ulnar nerve territory. Battiston
a
and Lanzetta described the use of the palmar sensory
[53]
branch of the median nerve to the sensory component
[56]
of the ulnar nerve. Brown et al. used the sensory
component to the third web space as a donor to the
fourth web space, coupled in an end‑to‑end fashion, while
the dorsal sensory branch of the ulnar nerve was sutured
to the sensory part of the median nerve in an end‑to‑side
b manner after performing an epineural window.
Figure 6: Ulnar nerve deficit. (a) Preoperative drawing showing the In 2011, Flores described a similar technique but instead
[61]
course of the motor branch of the ulnar nerve, and the terminal branch of an end‑to‑end anastomosis, he sutured the sensory
of the anterior interosseous nerve into the pronator quadrates; (b) the
ulnar nerve and its motor branch after extensive neurolysis component of the ulnar nerve in an end‑to‑side manner
to the sensory nerve of the third web space without an
epineural window. The author noted that at this level the
epineural layer is thin and that the microsurgical sutures
represent a sufficient trauma to stimulate the necessary
sprouting into the donor’s nerve. Oberlin et al. used
[62]
the LACN as a donor in the forearm, coapted to the dorsal
branch of the ulnar nerve by an interpositional nerve
graft harvested from the sural nerve. In his two cases, he
was able to avoid donor site morbidity when using donor
sensory nerves from the median nerve territory in the hand.
Ruchelsman et al. revised this technique by use of a
[63]
longer dissection of the LACN in the forearm and suturing it
without an inter positional graft in an end‑to‑side fashion to
the ulnar nerve before the take‑off of the sensory branch.
Figure 7: Terminal branch of the anterior interosseous nerve in the CONCLUSION
pronator quadratus muscle
The numerous advantages offered by transposing a
the hook of the hamate. Once the point of divergence functional nerve stump in proximity to a target muscle or
is identified, the motor nerve is followed proximally by skin territory have created new and exciting alternatives
blunt dissection. As reported by Sukegawa et al., this is for the management of nerve injuries, particularly
[57]
usually possible for about 33 mm. Sharp dissection is then those occurring far proximal in the arm or the brachial
required for an average of 19 mm. A longitudinal vascular plexus. Some of these options have been described only
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 4 || Jul 15, 2015 199