Page 208 - Read Online
P. 208
In this case the AIN needs to be traced proximally in
order to reach comfortably the motor branch to the
supinator. [15,41,42]
Schematic description: the AIN is identified in the
forearm. A lazy‑S incision is made over the volar aspect of
the mid‑forearm, and the lacertus fibrosus is divided. The
tendon of the superficial part of the PT is lengthened to
allow the muscle to be retracted, and the median nerve
exposed. The AIN lies on the radial side of the median
nerve and does not always course as a distinct fascicle.
A longitudinal vessel often demarcates it from the rest
of the median nerve. Once isolated, it should be traced
proximally to obtain enough length for a tension‑free
suture. The motor branch to the ECRB is then identified
under the brachioradialis muscle, coursing close to the
sensory branch of the radial nerve. This is followed as
distal as possible and then rotated toward the AIN. In case
of a size mismatch, the radial nerve is isolated proximally
in order to include the motor branch to the supinator,
which in turn will reach the AIN if appropriate proximal
dissection is completed.
In the event of isolated AIN palsy, an intra‑median nerve
transfer can be considered with redirection of branches to
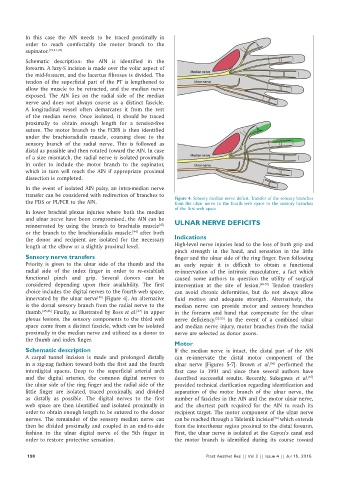
the FDS or PL/FCR to the AIN. Figure 4: Sensory median nerve deficit. Transfer of the sensory branches
from the ulnar nerve to the fourth web space to the sensory branches
of the first web space
In lower brachial plexus injuries where both the median
and ulnar nerve have been compromised, the AIN can be
[43]
reinnervated by using the branch to brachialis muscle ULNAR NERVE DEFICITS
or the branch to the brachioradialis muscle, after both
[44]
the donor and recipient are isolated for the necessary Indications
length at the elbow or a slightly proximal level. High‑level nerve injuries lead to the loss of both grip and
pinch strength in the hand, and sensation in the little
Sensory nerve transfers finger and the ulnar side of the ring finger. Even following
Priority is given to the ulnar side of the thumb and the an early repair it is difficult to obtain a functional
radial side of the index finger in order to re‑establish re‑innervation of the intrinsic musculature, a fact which
functional pinch and grip. Several donors can be caused some authors to question the utility of surgical
considered depending upon their availability. The first intervention at the site of lesion. [48‑51] Tendon transfers
choice includes the digital nerves to the fourth web space, can avoid chronic deformities, but do not always allow
innervated by the ulnar nerve [Figure 4]. An alternative fluid motion and adequate strength. Alternatively, the
[15]
is the dorsal sensory branch from the radial nerve to the median nerve can provide motor and sensory branches
thumb. [45,46] Finally, as illustrated by Ross et al. in upper in the forearm and hand that compensate for the ulnar
[47]
plexus lesions, the sensory components to the third web nerve deficiency. [52‑55] In the event of a combined ulnar
space come from a distinct fascicle, which can be isolated and median nerve injury, motor branches from the radial
proximally in the median nerve and utilized as a donor to nerve are selected as donor axons.
the thumb and index finger.
Motor
Schematic description If the median nerve is intact, the distal part of the AIN
A carpal tunnel incision is made and prolonged distally can re‑innervate the distal motor component of the
in a zig‑zag fashion toward both the first and the fourth ulnar nerve [Figures 5‑7]. Brown et al. performed the
[56]
interdigital spaces. Deep to the superficial arterial arch first case in 1991 and since then several authors have
and the digital arteries, the common digital nerves to described successful results. Recently, Sukegawa et al.
[57]
the ulnar side of the ring finger and the radial side of the provided technical clarification regarding identification and
little finger are isolated, traced proximally, and divided separation of the motor branch of the ulnar nerve, the
as distally as possible. The digital nerves to the first number of fascicles in the AIN and the motor ulnar nerve,
web space are then identified and isolated proximally in and the shortest path required for the AIN to reach its
order to obtain enough length to be sutured to the donor recipient target. The motor component of the ulnar nerve
[58]
nerves. The remainder of the sensory median nerve can can be reached through a Taleisnik incision which extends
then be divided proximally and coupled in an end‑to‑side from the interthenar region proximal to the distal forearm.
fashion to the ulnar digital nerve of the 5th finger in First, the ulnar nerve is isolated at the Guyon’s canal and
order to restore protective sensation. the motor branch is identified during its course toward
198 Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 4 || Jul 15, 2015