Page 44 - Read Online
P. 44
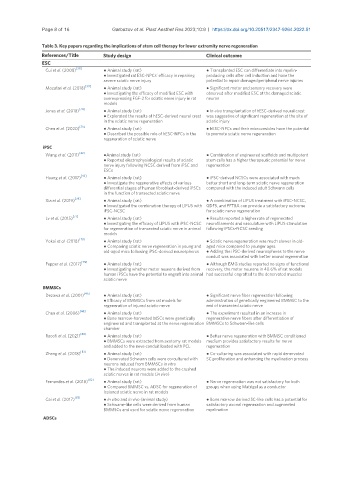
Page 8 of 16 Garbuzov et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:9 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2022.51
Table 3. Key papers regarding the implications of stem cell therapy for lower extremity nerve regeneration
References/Title Study design Clinical outcome
ESC
Cui et al. (2008) [38] ● Animal study (rat) ● Transplanted ESC can differentiate into myelin-
● Investigated rat ESC-NPCs’ efficacy in repairing producing cells after cell induction and have the
severe sciatic nerve injury potential to repair damaged peripheral nerve injuries
Mozafari et al. (2018) [39] ● Animal study (rat) ● Significant motor and sensory recovery were
● Investigating the efficacy of modified ESC with observed after modified ESC at the damaged sciatic
overexpressing FGF-2 for sciatic nerve injury in rat neuron
models
[74]
Jones et al. (2018) ● Animal study (rat) ● In-vivo transplantation of hESC-derived neural crest
● Explorated the results of hESC-derived neural crest was suggestive of significant regeneration at the site of
in the sciatic nerve regeneration sciatic injury
[75]
Chen et al. (2020) ● Animal study (rat) ● hESC-NPCs and their microvesicles have the potential
● Described the possible role of hESC-NPCs in the to promote sciatic nerve regeneration
regeneration of sciatic nerve
iPSC
[42]
Wang et al. (2011) ●Animal study (rat) ● Combination of engineered scaffolds and multipotent
● Reported electrophysiological results of sciatic stem cells has a higher therapeutic potential for nerve
nerve injury following NCSC derived from iPSC and regeneration
ESCs
Huang et al. (2017) [43] ● Animal study (rat) ● iPSC-derived NCSCs were associated with much
● Investigate the regenerative effects of various better short and long-term sciatic nerve regeneration
differential stages of human fibroblast-derived iPSCs compared with the induced adult Schwann cells
in the function of transected sciatic nerve
[76]
Xia et al. (2019) ● Animal study (rat) ● A combination of LIPUS treatment with iPSC-NCSC,
● Investigated the combination therapy of LIPUS with GDF5, and PFTBA can provide a satisfactory outcome
iPSC-NCSC for sciatic nerve regeneration
Lv et al. (2015) [77] ● Animal study (rat) ● Results reported a higher rate of regenerated
● Investigating the efficacy of LIPUS with iPSC-NCSC neurofilaments and vasculature with LIPUS stimulation
for regeneration of transected sciatic nerve in animal following iPSCs-NCSC seeding
models
[78]
Yokoi et al. (2018) ● Animal study (rat) ● Sciatic nerve regeneration was much slower in old-
● Comparing sciatic nerve regeneration in young and aged mice compared to younger ages.
old-aged mice following iPSC-derived neurospheres ● Adding the iPSC-derived neurospheres to the nerve
conduit was associated with better axonal regeneration
Pepper et al. (2017) [79] ● Animal study (rat) ● Although EMG studies reported no signs of functional
● Investigating whether motor neurons derived from recovery, the motor neurons in 40.6% of rat models
human iPSCs have the potential to engraft into animal had successful engrafted to the denervated muscles
sciatic nerve
BMMSCs
[45]
Dezawa et al. (2001) ● Animal study (rat) ● Significant nerve fiber regeneration following
● Efficacy of BMMSCs from rat models for administration of genetically engineered BMMSC to the
regeneration of injured sciatic nerve end of transected sciatic nerve
[46]
Chen et al. (2006) ● Animal study (rat) ● The experiment resulted in an increase in
● Bone marrow-harvested MSCs were genetically regenerative nerve fibers after differentiation of
engineered and transplanted at the nerve regeneration BMMSCs to Schwann-like cells
chamber
Raoofi et al. (2021) [80] ● Animal study (rat) ● Better nerve regeneration with BMMSC conditioned
● BMMSCs were extracted from axotomy rat models medium provides satisfactory results for nerve
and added to the neve conduit loaded with PCL regeneration
Zheng et al. (2018) [81] ● Animal study (rat) ● Co-culturing was associated with rapid denervated
● Denervated Schwann cells were co-cultured with SC proliferation and enhancing the myelination process
neurons induced from BMMSCs in vitro
● The induced neurons were added to the crushed
sciatic nerves in rat models (in vivo)
Fernandes et al. (2018) [82] ● Animal study (rat) ● Nerve regeneration was not satisfactory for both
● Compared BMMSC vs. ADSC for regeneration of groups when using Matrigel as a conductor
lesioned sciatic nerve in rat models
Cai et al. (2017) [83] ● In vitro and in vivo (animal study) ● Bone marrow derived SC-like cells has a potential for
● Schwann-like cells were derived from human satisfactory axonal regeneration and augmented
BMMSCs and used for sciatic nerve regeneration myelination
ADSCs