Page 43 - Read Online
P. 43
Garbuzov et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:9 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2022.51 Page 7 of 16
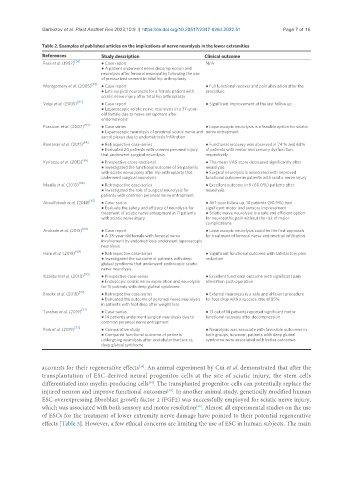
Table 2. Examples of published articles on the implications of nerve neurolysis in the lower extremities
References Study description Clinical outcome
Pess et al. (1987) [36] ● Case report N/A
● A patient underwent nerve decompression and
neurolysis after femoral neuropathy following the use
of pressurized cement in total hip arthroplasty
[61]
Montgomery et al. (2005) ● Case report ● Full functional recover and pain alleviation after the
● Late surgical neurolysis for a female patient with procedure
sciatic nerve injury after total hip arthroplasty
[62]
Volpi et al. (2005) ● Case report ● Significant improvement at the last follow up
● Laparoscopic sciatic nerve neurolysis in a 37-year-
old female due to nerve entrapment after
endometriosis
Possover et al. (2007) [63] ● Case series ● Laparoscopic neurolysis is a feasible option for sciatic
● Laparoscopic neurolysis of proximal sciatic nerve and nerve entrapment
sacral plexus due to endometriosis infiltration
[64]
Ramanan et al. (2011) ● Retrospective case-series ● Functional recovery was observed in 74 % and 68%
● Evaluated 20 patients with commo peroneal injury of patients with motor and sensory dysfunction,
that underwent surgical neurolysis respectively
[65]
Kyriacou et al. (2013) ● Prospective cross-sectional ● The mean VAS score decreased significantly after
● Investigated the functional outcome of 56 patients neurolysis
with sciatic nerve palsy after hip arthroplasty that ● Surgical neurolysis is associated with improved
underwent surgical neurolysis functional outcome in patients with sciatic nerve injury
Maalla et al. (2013) [66] ● Retrospective case-series ● Excellent outcome in 9 (60.0%) patients after
● Investigated the role of surgical neurolysis for neurolysis
patients with common peroneal nerve entrapment
Aboulfetouh et al. (2014) [67] ● Case-series ● At 1-year follow up, 10 patients (90.9%) had
● Evaluate the safety and efficacy of neurolysis for significant motor and sensory improvement
treatment of sciatic nerve entrapment in 11 patients ● Sciatic nerve neurolysis is a safe and efficient option
with sciatic nerve injury for neuropathic pain without the risk of major
complications
[68]
Andrade et al. (2015) ● Case report ● Laparoscopic neurolysis could be the first approach
● A 38-year-old female with femoral nerve for treatment of femoral nerve endometrial infiltration
involvement by endometriosis underwent laparoscopic
neurolysis
[69]
Ham et al. (2018) ● Retrospective case-series ● Significant functional outcome with satisfactory pain
● Investigated the outcome of patients with deep reduction
gluteal syndrome that underwent endoscopic sciatic
nerve neurolysis
[70]
Ilizaliturri et al. (2018) ● Prospective case-series ● Excellent functional outcome with significant pain
● Endoscopic sciatic nerve exploration and neurolysis alleviation post-operation
for 15 patients with deep gluteal syndrome
[71]
Broekx et al. (2018) ● Retrospective case-series ● External neurolysis is a safe and efficient procedure
● Evaluated the outcome of peroneal nerve neurolysis for foot drop with a success rate of 85%
in patients with foot drop after weight loss
[72]
Tarabay et al. (2019) ● Case-series ● 13 out of 14 patients reported significant motor
● 14 patients underwent surgical neurolysis due to functional recovery after decompression
common peroneal nerve entrapment
[73]
Park et al. (2019) ● Comparative study ● Neurolysis was associate with favorable outcomes in
● Compared functional outcome of patients both groups; however, patients with deep gluteal
undergoing neurolysis after acetabular fracture vs. syndrome were associated with better outcomes
deep gluteal syndrome
accounts for their regenerative effects . An animal experiment by Cui et al. demonstrated that after the
[38]
transplantation of ESC-derived neural progenitor cells at the site of sciatic injury, the stem cells
[38]
differentiated into myelin-producing cells . The transplanted progenitor cells can potentially replace the
injured neuron and improve functional outcomes . In another animal study, genetically modified human
[38]
ESC overexpressing fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) was successfully employed for sciatic nerve injury,
which was associated with both sensory and motor resolution . Almost all experimental studies on the use
[39]
of ESCs for the treatment of lower extremity nerve damage have pointed to their potential regenerative
effects [Table 3]. However, a few ethical concerns are limiting the use of ESC in human subjects. The main