Page 69 - Read Online
P. 69
be concerned is that anxiety was significantly higher in the
group of radiotherapy, especially in women. [29]
Among psychosocial issues, depression is the most prevalent
in cancer patients, and it is the most common reason for
referral to a mental health professional in oncology. In head
and neck cancer, depression rates can reach 43% before
treatment and 44% after treatment, which is particularly
elevated compared with all oncology patients, in whom
depression rates vary between 20 and 30% at any one time. [34]
Depression is underdiagnosed and the consequence
includes impaired quality of life, treatment noncompliance,
and increased length of hospital stay, greater health care
utilization, and suicide. Taking into account that HNSCC
survivors rank among the top three cancers with the highest
rates of suicide, after lung and stomach cancer, the main
interest about target depression as a main QOL-outcome is
the powerful to be prevented or treated using psychotherapy
and/or pharmacologic therapy. [35,36]
[37]
Moubayed et al. established a study including 209
patients with HNSCC and they analysed the results of a few
questionnaires to determine the presence of depression and
its impact in their quality of life. They identified 4 independent
predictors of long-term depressive symptoms after controlling
for all patient, tumour and treatment factors. They include
the following pre-treatment factors: (1) having more than 3
medications; (2) smoking at diagnosis; (3) having more than
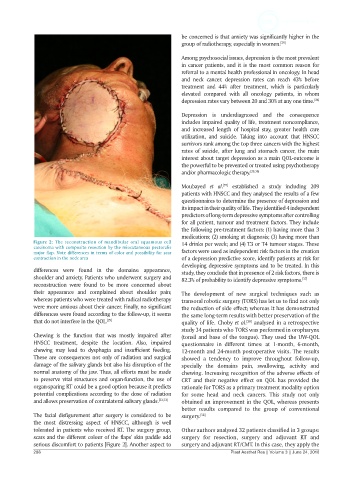
Figure 2: The reconstruction of mandibular oral squamous cell 14 drinks per week; and (4) T3 or T4 tumour stages. These
carcinoma with composite resection by the miocutaneous pectoralis
major flap. Note differences in terms of color and possibility for scar factors were used as independent risk factors in the creation
contraction in the neck area of a depression predictive score, identify patients at risk for
developing depressive symptoms and to be treated. In this
differences were found in the domains: appearance, study, they conclude that in presence of 2 risk factors, there is
shoulder and anxiety. Patients who underwent surgery and 82.3% of probability to identify depressive symptoms. [37]
reconstruction were found to be more concerned about
their appearance and complained about shoulder pain; The development of new surgical techniques such as
whereas patients who were treated with radical radiotherapy transoral robotic surgery (TORS) has let us to find not only
were more anxious about their cancer. Finally, no significant the reduction of side effect; whereas it has demonstrated
differences were found according to the follow-up, it seems the same long-term results with better preservation of the
that do not interfere in the QOL. [29] quality of life. Choby et al. analysed in a retrospective
[38]
study 34 patients who TORS was performed in oropharynx
Chewing is the function that was mostly impaired after (tonsil and base of the tongue). They used the UW-QOL
HNSCC treatment, despite the location. Also, impaired questionnaire in different times: at 1-month, 6-month,
chewing may lead to dysphagia and insufficient feeding. 12-month and 24-month postoperative visits. The results
These are consequences not only of radiation and surgical showed a tendency to improve throughout follow-up,
damage of the salivary glands but also his disruption of the specially the domains pain, swallowing, activity and
normal anatomy of the jaw. Thus, all efforts must be made chewing. Increasing recognition of the adverse effects of
to preserve vital structures and organ-function, the use of CRT and their negative effect on QOL has provided the
organ-sparing RT could be a good option because it predicts rationale for TORS as a primary treatment modality option
potential complications according to the dose of radiation for some head and neck cancers. This study not only
and allows preservation of contralateral salivary glands. [32,33] obtained an improvement in the QOL, whereas presents
better results compared to the group of conventional
The facial disfigurement after surgery is considered to be surgery. [38]
the most distressing aspect of HNSCC, although is well
tolerated in patients who received RT. The surgery group, Other authors analysed 32 patients classified in 3 groups:
scars and the different colour of the flaps’ skin paddle add surgery for resection, surgery and adjuvant RT and
serious discomfort to patients [Figure 2]. Another aspect to surgery and adjuvant RT/CMT. In this case, they apply the
208 Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || June 24, 2016