Page 69 - Read Online
P. 69
The authors report two cases of ulnar nerve injury was performed on the 4th and 5th digits. The hand was
proximal to the elbow: a double end‑to‑side coaptation casted for immobilization, and the elbow was maintained
through a nerve graft allowed axons from the donor in semi‑extended position for 20 days, followed by
median nerve to rehabilitate the recipient ulnar nerve progressive elbow mobilization.
(a surgically induced Martin Gruber anastomosis). This The Highet‑Zachary scheme was applied for motor
model was recently proposed by Kayikcioglu et al. and evaluation, and a modification of Mackinnon et al. [1]
[9]
Magdi Sherif and Amr. In our cases, proximal ulnar Sensory recovery scale was used with static and moving
[10]
nerve repair was performed through a long traditional 2‑point discrimination test. Early (20 days) protective
nerve graft by end‑to‑end coaptation in the former, and sensation recovery was registered, but the 36‑month
by neurolysis in the latter. In both cases, a Zancolli lasso and 6‑year follow‑up showed poor outcomes both for
procedure was added distally. Our results are compared to sensation (S1) and motion (M0).
six cases that were previously published and the effects
of injury type, time from the initial trauma, surgical Case 2
techniques, and future perspectives are discussed. A 46‑year‑old man presented with proximal ulnar nerve
injuries following a high voltage injury to the upper
CASE REPORT third of his left forearm. Three months after trauma, an
electrophysiological study was performed which showed
Case 1 the absent motor and sensory potentials. An extensive
A 22‑year‑old man, a hand worker, presented with surgical exposure and external neurolysis were performed
proximal left ulnar nerve injury. He was found to have together with distal babysitting technique. The terminal
head trauma and an open contaminated wound of the left branch of the cutaneous medialis antebrachii was taken
elbow with more than 12 cm of missing ulnar nerve. The during ulnar exposure, and it was used as bridge graft
wound was found to be contaminated with Actinobacter without nerve stimulation; a Zancolli lasso procedure was
baumanii. Extensive debridement of the wound was carried also performed on the fourth and fifth digits. After two
out, and a cable graft from the sural nerve was performed weeks, sensory and motor rehabilitation began following
1 month after. A small remnant of the cutaneous medialis the same protocol applied to the first patient.
antebrachii nerve was found during scar removal, and it Outcome evaluation was performed as in case 1. Also in
was used for the babysitting procedure. this case, early protective sensation recovery (24 days)
At the distal third of the volar aspect of the forearm, was registered at 12‑month follow‑up. This high‑voltage
5 cm proximal to the distal palmar wrist crease, almost injury showed good results (S5 and M4) at 12‑month
4 cm of both the median and the ulnar nerve were follow‑up.
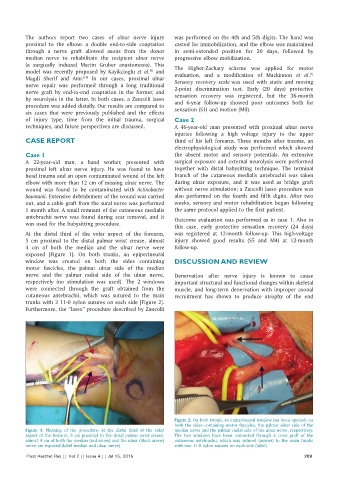
exposed [Figure 1]. On both trunks, an epiperineural
window was created on both the sides containing DISCUSSION AND REVIEW
motor fascicles, the palmar ulnar side of the median
nerve and the palmar radial side of the ulnar nerve, Denervation after nerve injury is known to cause
respectively (no stimulation was used). The 2 windows important structural and functional changes within skeletal
were connected through the graft obtained from the muscle, and long‑term denervation with improper axonal
cutaneous antebrachii, which was sutured to the main recruitment has shown to produce atrophy of the end
trunks with 2 11‑0 nylon sutures on each side [Figure 2].
Furthermore, the “lasso” procedure described by Zancolli
Figure 2: On both trunks, an epiperineural window has been opened, on
both the sides containing motor fascicles, the palmar ulnar side of the
Figure 1: Planning of the procedure: at the distal third of the volar median nerve and the palmar radial side of the ulnar nerve, respectively.
aspect of the forearm, 5 cm proximal to the distal palmar wrist crease, The two windows have been connected through a cross graft of the
almost 4 cm of both the median (red arrow) and the ulnar (black arrow) cutaneous antebrachii, which was sutured (arrows) to the main trunks
nerve are exposed (label median and ulnar nerve) with two 11‑0 nylon sutures on each side (label)
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 2 || Issue 4 || Jul 15, 2015 209