Page 46 - Read Online
P. 46
Page 4 of 12 Wee et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2019;6:12 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2019.02
A B
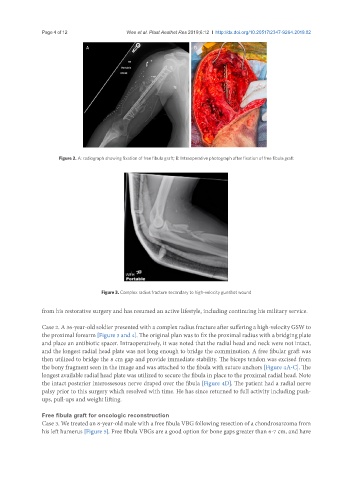
Figure 2. A: radiograph showing fixation of free fibula graft; B: Intraoperative photograph after fixation of free fibula graft
Figure 3. Complex radius fracture secondary to high-velocity gunshot wound
from his restorative surgery and has resumed an active lifestyle, including continuing his military service.
Case 2. A 36-year-old soldier presented with a complex radius fracture after suffering a high-velocity GSW to
the proximal forearm [Figure 3 and 4]. The original plan was to fix the proximal radius with a bridging plate
and place an antibiotic spacer. Intraoperatively, it was noted that the radial head and neck were not intact,
and the longest radial head plate was not long enough to bridge the comminution. A free fibular graft was
then utilized to bridge the 8 cm gap and provide immediate stability. The biceps tendon was excised from
the bony fragment seen in the image and was attached to the fibula with suture anchors [Figure 4A-C]. The
longest available radial head plate was utilized to secure the fibula in place to the proximal radial head. Note
the intact posterior interossesous nerve draped over the fibula [Figure 4D]. The patient had a radial nerve
palsy prior to this surgery which resolved with time. He has since returned to full activity including push-
ups, pull-ups and weight lifting.
Free fibula graft for oncologic reconstruction
Case 3. We treated an 8-year-old male with a free fibula VBG following resection of a chondrosarcoma from
his left humerus [Figure 5]. Free fibula VBGs are a good option for bone gaps greater than 6-7 cm, and have