Page 16 - Read Online
P. 16
Tejiram et al. Plast Aesthet Res. 2025;12:9 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2024.109 Page 11 of 16
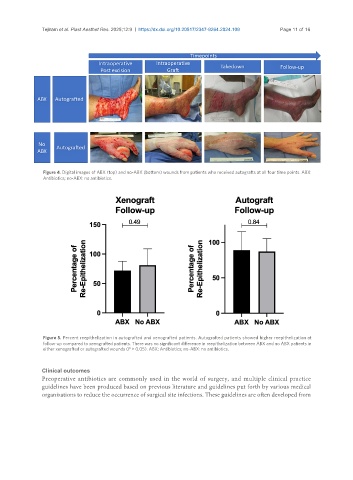
Figure 4. Digital images of ABX (top) and no-ABX (bottom) wounds from patients who received autografts at all four time points. ABX:
Antibiotics; no-ABX: no antibiotics.
Figure 5. Percent reepithelization in autografted and xenografted patients. Autografted patients showed higher reepithelization at
follow-up compared to xenografted patients. There was no significant difference in reepithelization between ABX and no ABX patients in
either xenografted or autografted wounds (P > 0.05). ABX: Antibiotics; no-ABX: no antibiotics.
Clinical outcomes
Preoperative antibiotics are commonly used in the world of surgery, and multiple clinical practice
guidelines have been produced based on previous literature and guidelines put forth by various medical
organizations to reduce the occurrence of surgical site infections. These guidelines are often developed from